The reaction in which carbonyl group/ compound is first treated with hydrazine and than treated with base to produce alkane is called Wolf Kishner,s Reduction Reaction. In this reaction C=O group is converted into -CH2-group.
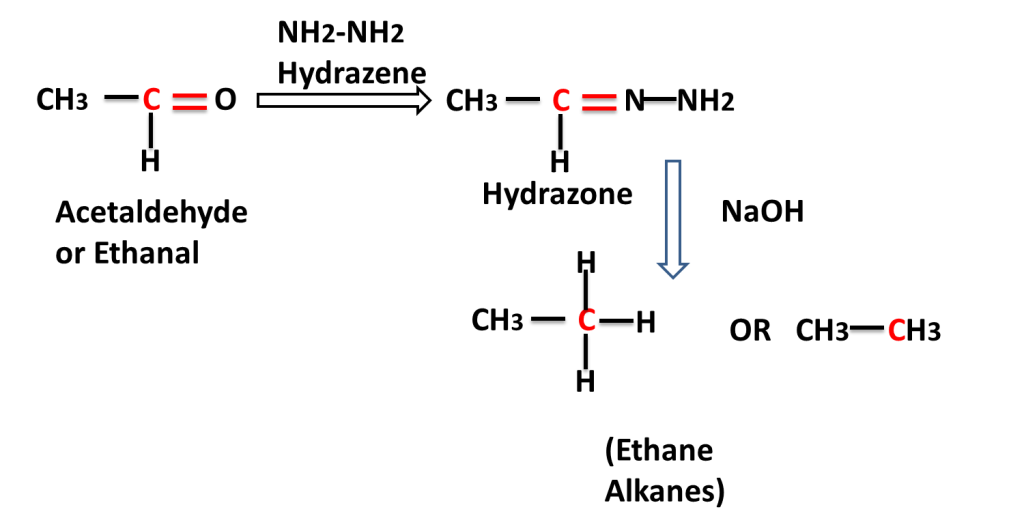
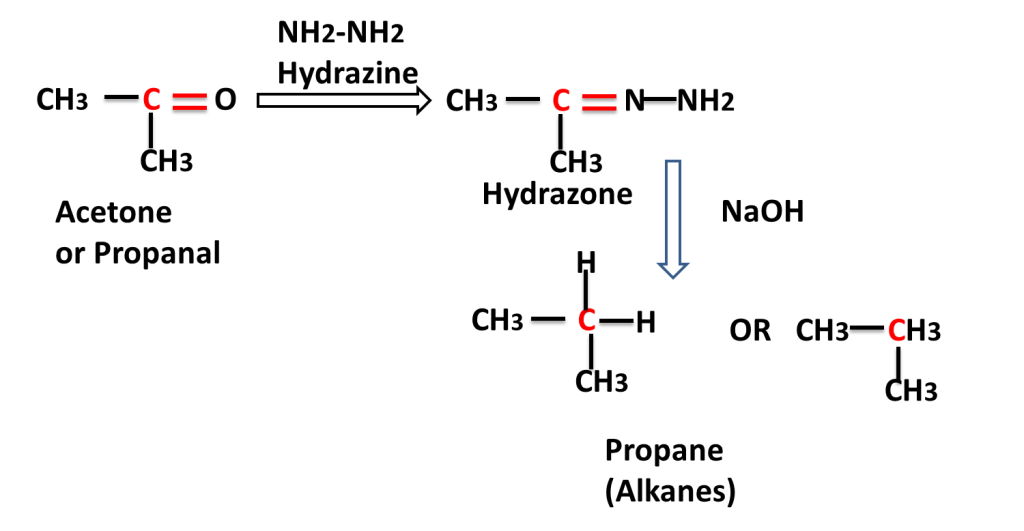
The reaction in which carbonyl group/ compound is first treated with hydrazine and than treated with base to produce alkane is called Wolf Kishner,s Reduction Reaction. In this reaction C=O group is converted into -CH2-group.


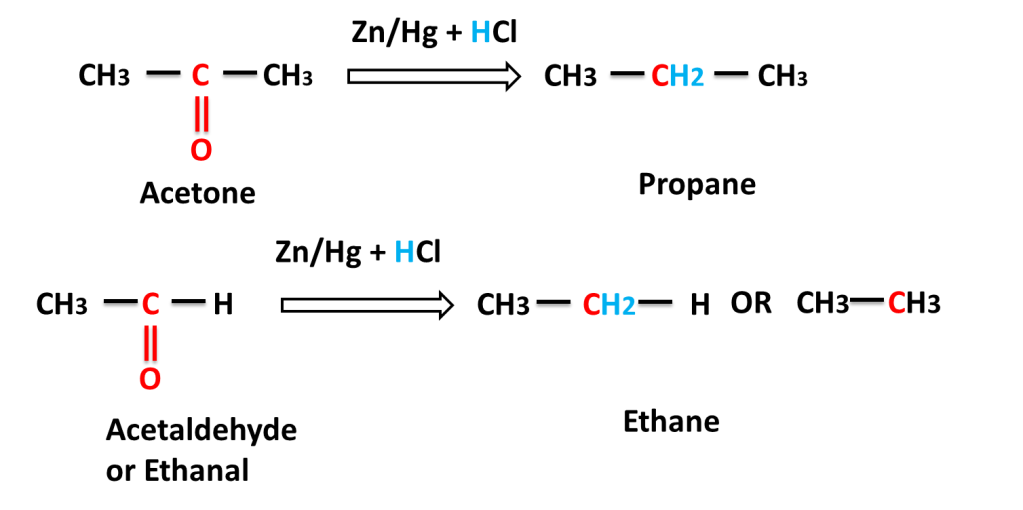
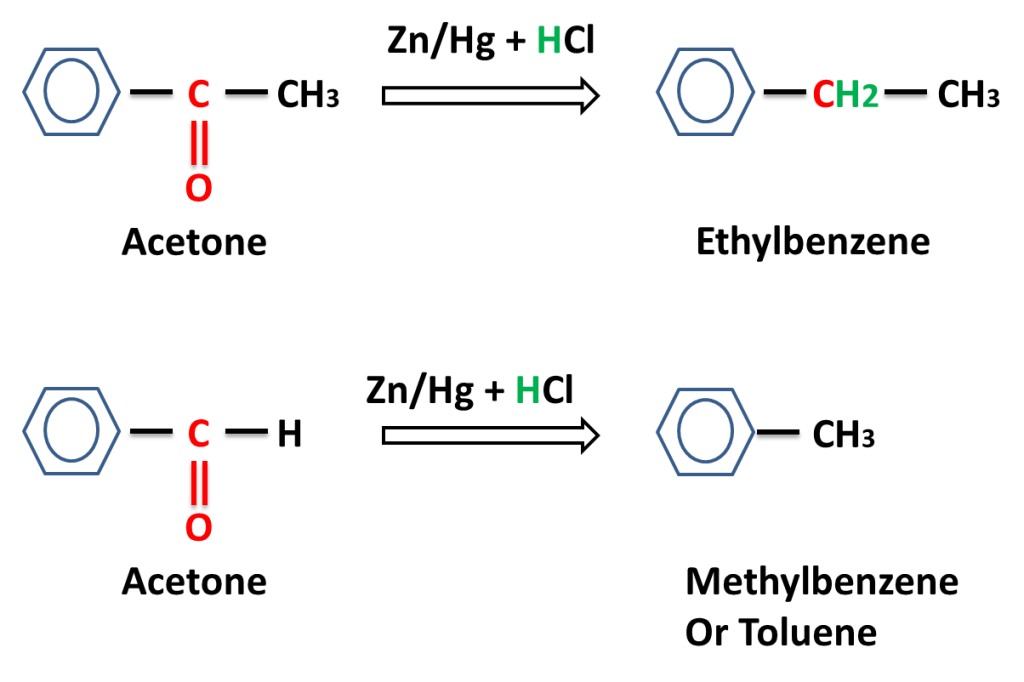
The reaction in which carbonyl group (C=O) is reduced into (-CH2-) group on reacting with a mixture of zinc and hydrochloric acid is called Clemmensen,s Reduction.
General reaction:-
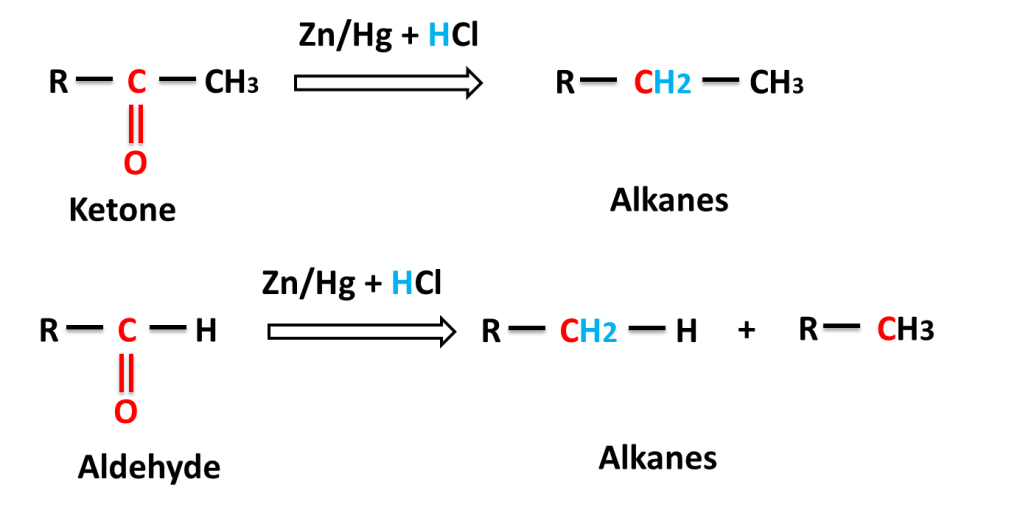
Reaction of aliphatic aldehyde and ketones-
Reaction of aromatic aldehyde and ketones-
Question:- Why did a mixture of Zn+HCl is used for reduction ?
Answer:- Zn reaction reacts with HCl to produce H2 gas which reduces carbonyl (C=O) to alkane (-CH2-).
Question:- Why does amalgam of Zinc (Zn/Hg) use in spite of only Zn ?
Answer:- Zn reacts with HCl to produce H2 very fast that move out fast from reaction mixture and carbonyl compound has very little time to react and most of hydrogen moves out of reaction mixture without reacting whereas in form of amalgam, Zn reacts slowly to produce hydrogen slowly, which can react with carbonyl compound. because only those Zn atoms reacts with HCl which are present on the surface of amalgam .
Amalgam: The solution of metal in mercury is called amalgam. Metal dissolve in mercury like salt dissolve in water.
In carbylamine reaction amine is treated with chloroform in presence of sodium hydroxide to produce isocyanide which has offensive / foul smell is called carbylamine reaction or isocyanide test.
This reaction is used to distinguish PRIMARY AMINE from SECONDARY / TERTIARY AMINE.
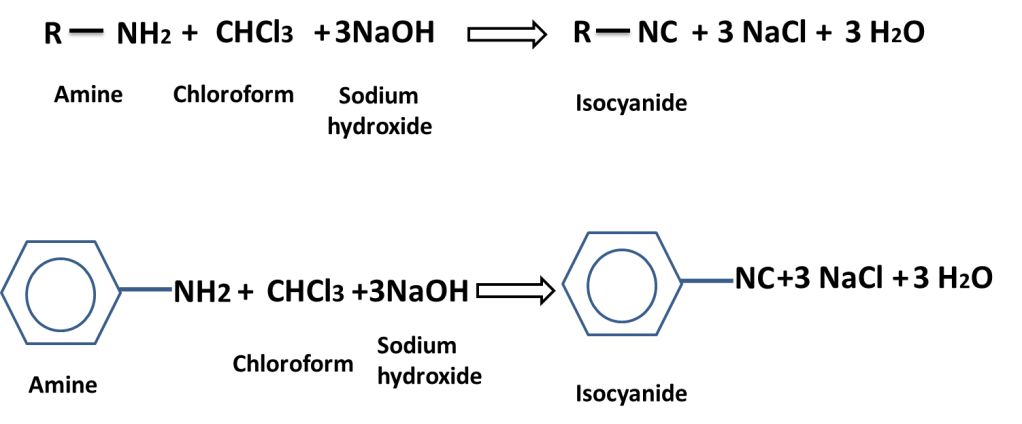
The isocyanide is poisonous gas, and Methyl isocyanide (CH3NC) that is also called MIC gas was leaked in Bhopal, Madhypradesh state of India from a multinational factory, consequently a large number of people were died and injured and have been suffering till now.
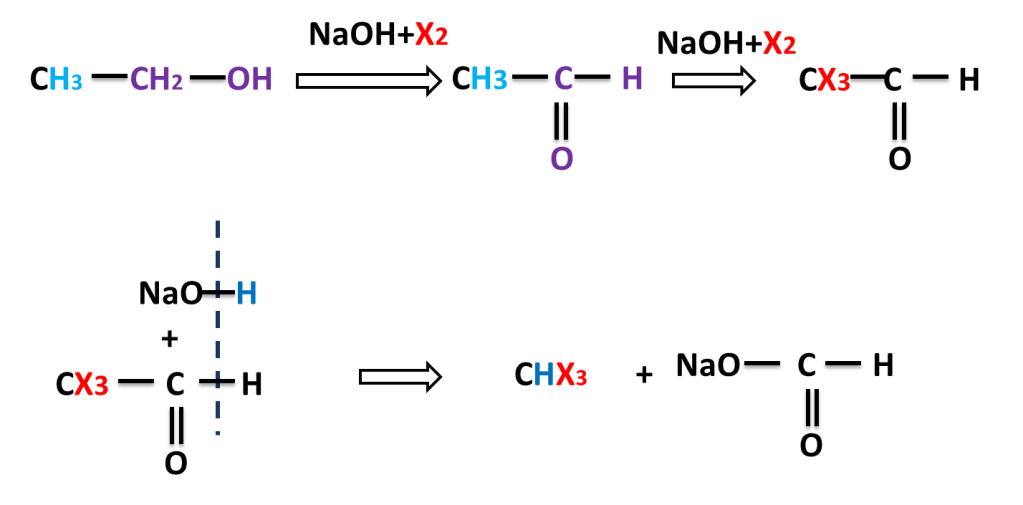
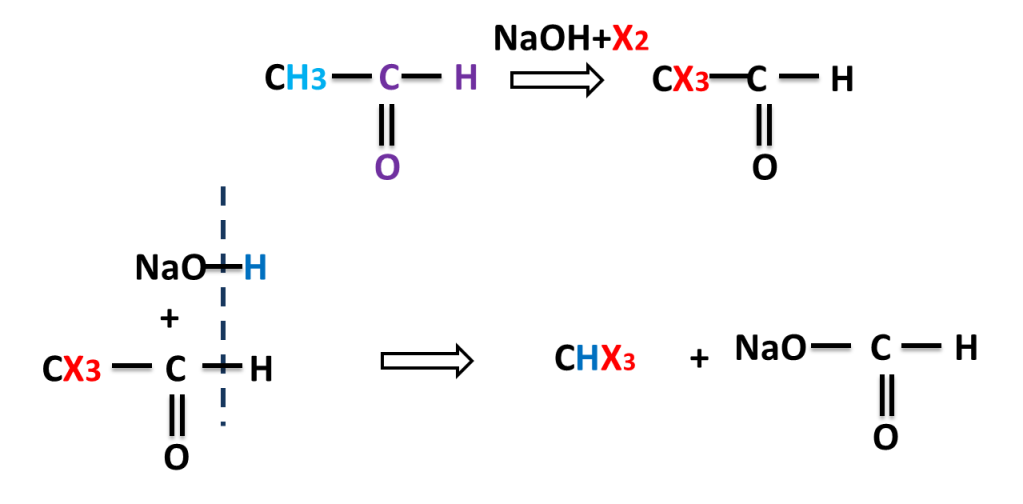
The reaction in which carbonyl compound having three alpha hydrogen treated with a mixture of halogen and sodium hydroxide to give haloform means trihalomethane.
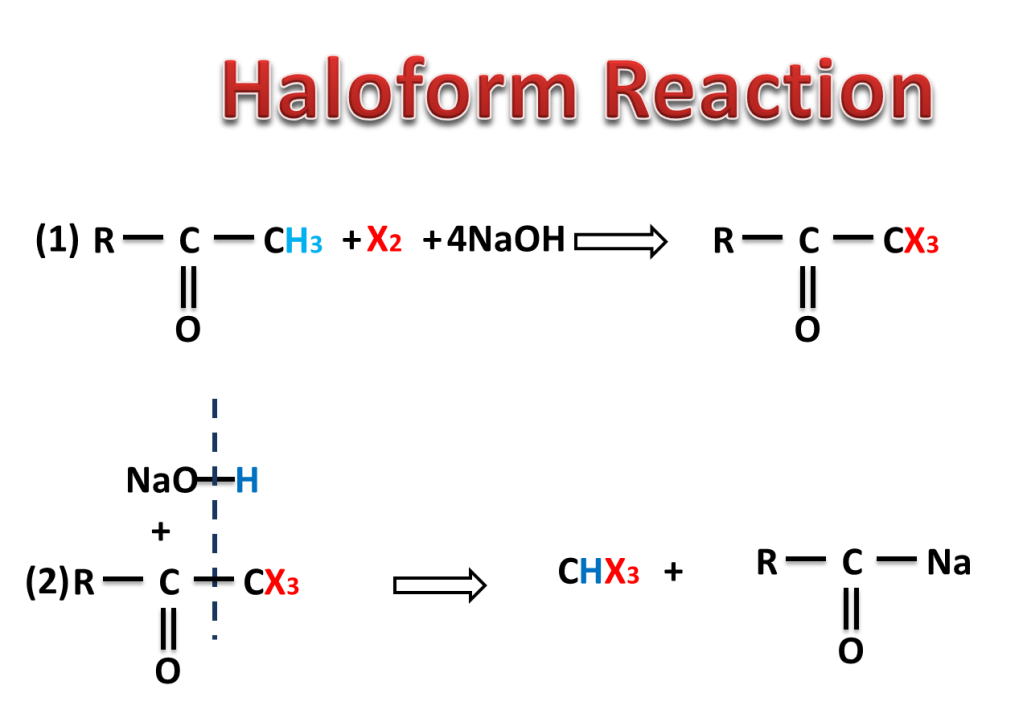
NaOH reacts with X2 to produce NaOI which replaces three hydrogen by three halogen atom. here halogens are Cl2, Br2 or I2.
Alpha, beta, gama and delta Carbon / Hydrogen .
1. First carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called ALPHA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called ALPHA hydrogen.
2. Second carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called BETA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called BETA hydrogen.
3. Third carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called GAMA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called GAMA hydrogen.
4. Forth carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called DELTA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called DELTA hydrogen.

Example of Haloform Reaction:-
Reaction of Ethanal ( Acetaldehyde)
Reaction of Propanone (Acetone)
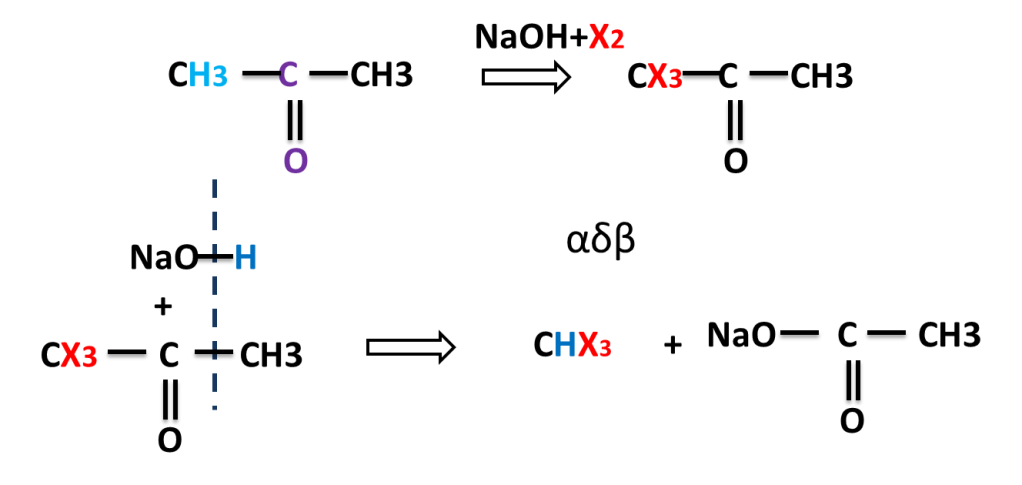
This reaction is also given by alcohol having three beta hydrogen atoms. alcohol is first converted into carbonyl compound than into haloform.