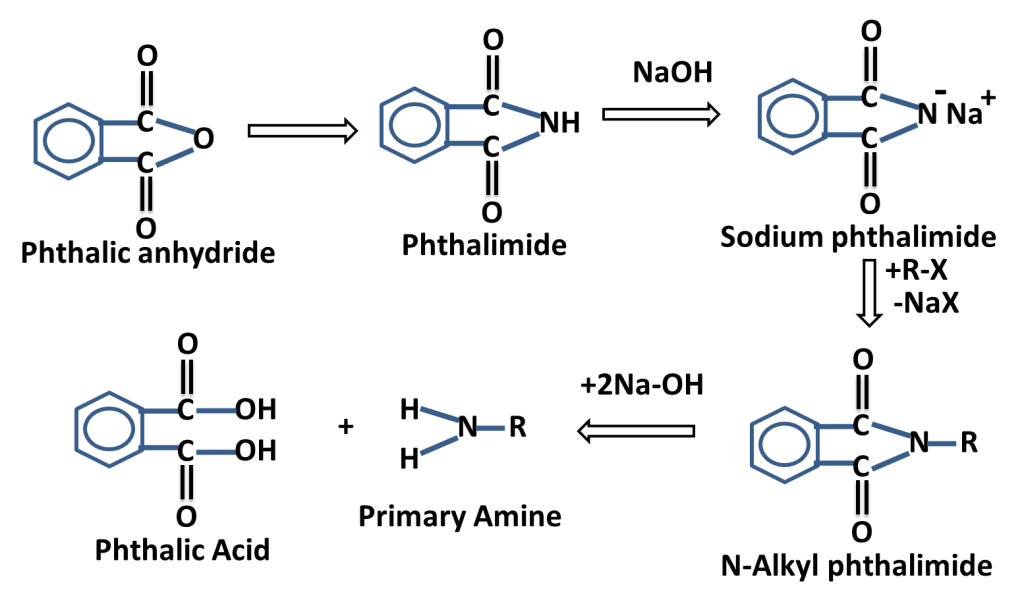
The reaction in which carbonyl group/ compound is first treated with hydrazine and than treated with base to produce alkane is called Wolf Kishner,s Reduction Reaction. In this reaction C=O group is converted into -CH2-group.
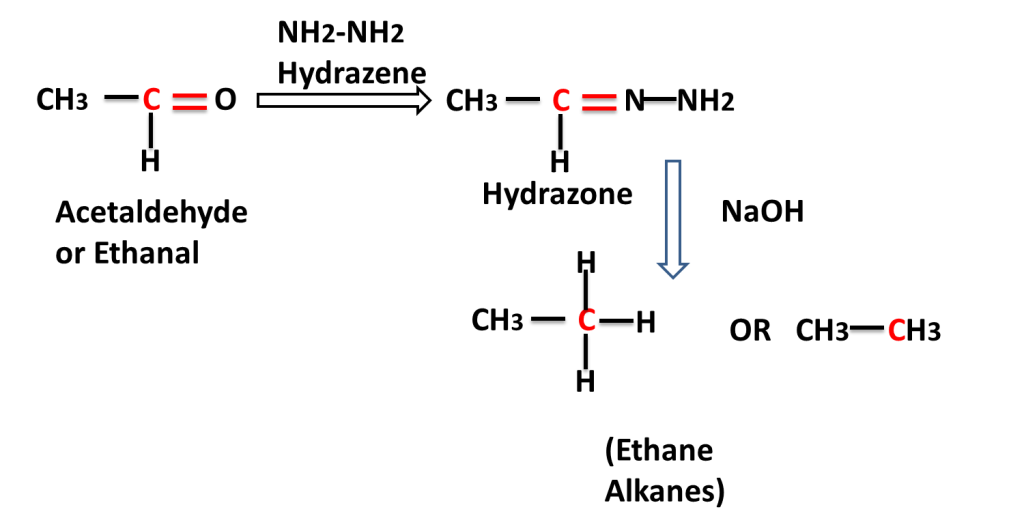
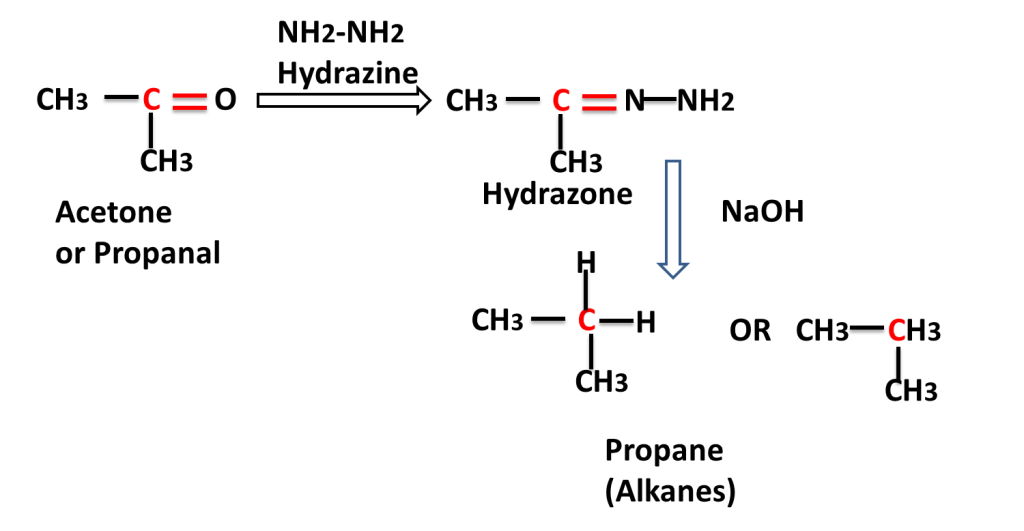
The reaction in which carbonyl group/ compound is first treated with hydrazine and than treated with base to produce alkane is called Wolf Kishner,s Reduction Reaction. In this reaction C=O group is converted into -CH2-group.


In carbylamine reaction amine is treated with chloroform in presence of sodium hydroxide to produce isocyanide which has offensive / foul smell is called carbylamine reaction or isocyanide test.
This reaction is used to distinguish PRIMARY AMINE from SECONDARY / TERTIARY AMINE.
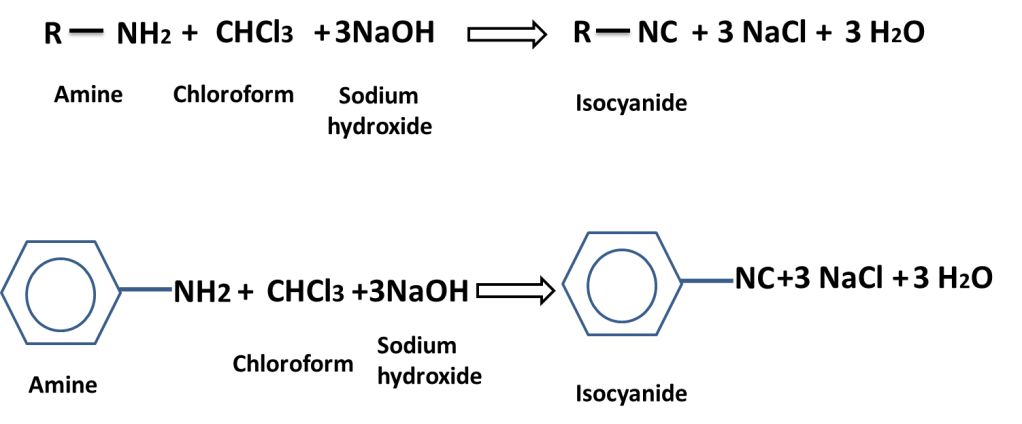
The isocyanide is poisonous gas, and Methyl isocyanide (CH3NC) that is also called MIC gas was leaked in Bhopal, Madhypradesh state of India from a multinational factory, consequently a large number of people were died and injured and have been suffering till now.
The reaction in which carbonyl compound having three alpha hydrogen treated with a mixture of halogen and sodium hydroxide to give haloform means trihalomethane.
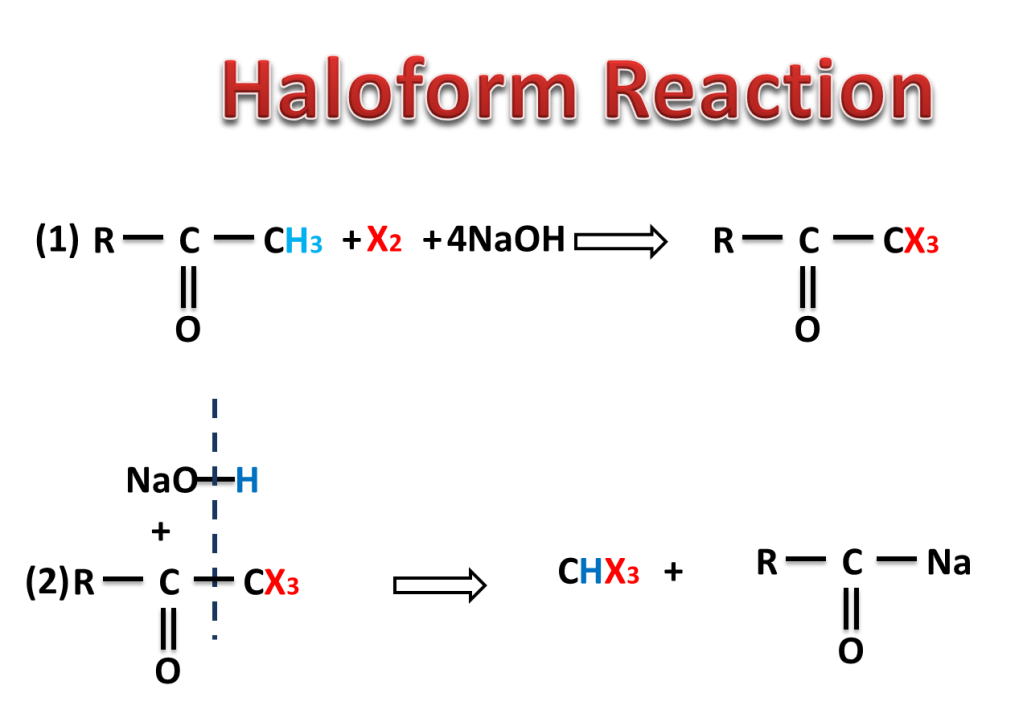
NaOH reacts with X2 to produce NaOI which replaces three hydrogen by three halogen atom. here halogens are Cl2, Br2 or I2.
Alpha, beta, gama and delta Carbon / Hydrogen .
1. First carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called ALPHA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called ALPHA hydrogen.
2. Second carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called BETA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called BETA hydrogen.
3. Third carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called GAMA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called GAMA hydrogen.
4. Forth carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called DELTA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called DELTA hydrogen.

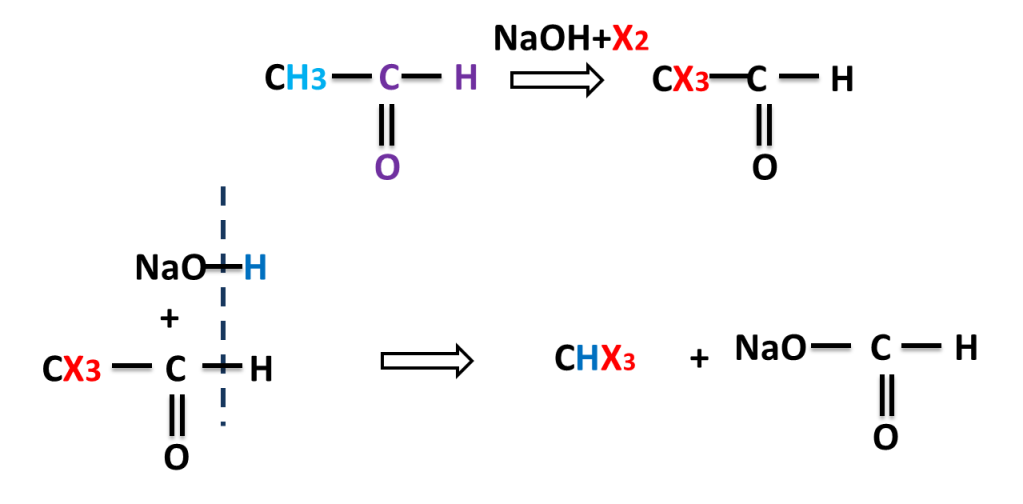
Example of Haloform Reaction:-
Reaction of Ethanal ( Acetaldehyde)
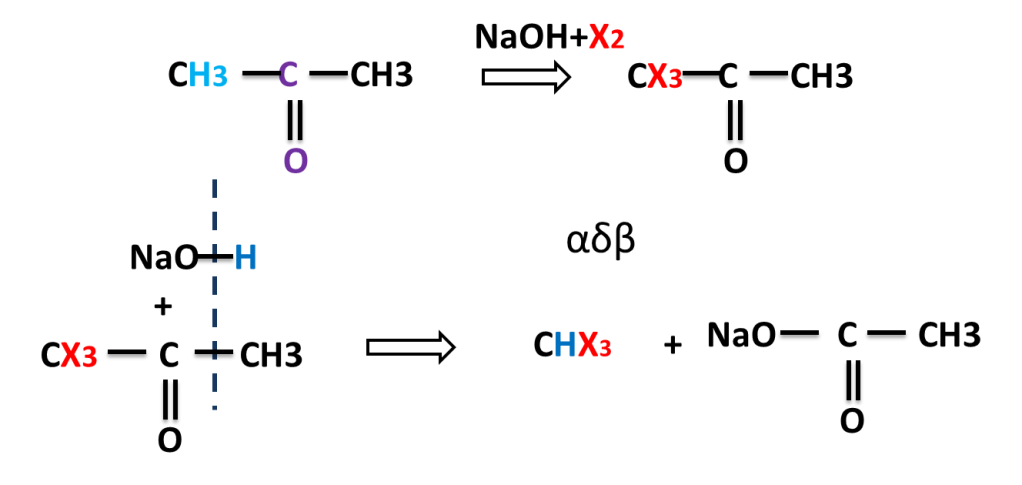
Reaction of Propanone (Acetone)
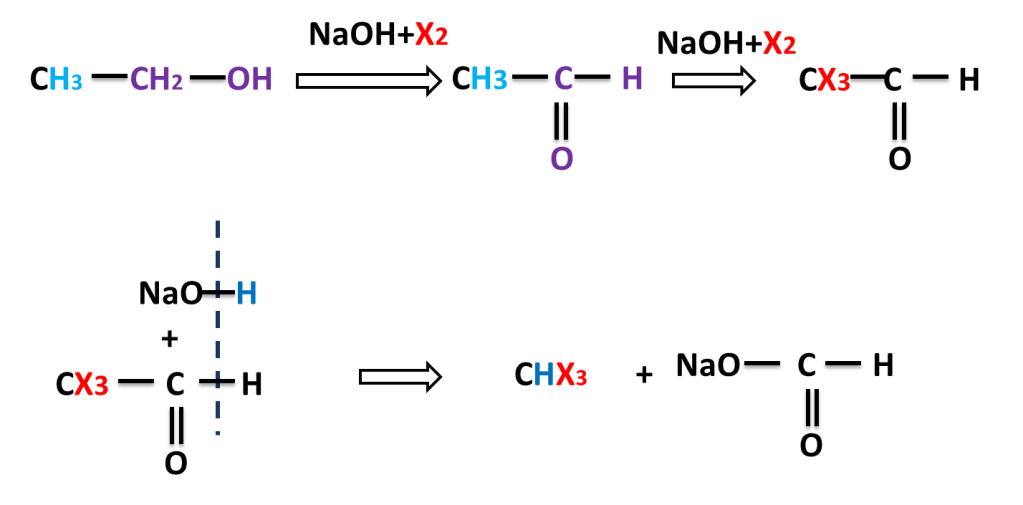
This reaction is also given by alcohol having three beta hydrogen atoms. alcohol is first converted into carbonyl compound than into haloform.
Alpha, beta, gama and delta Carbon / Hydrogen .
1. First carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called ALPHA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called ALPHA hydrogen.
2. Second carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called BETA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called BETA hydrogen.
3. Third carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called GAMA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called GAMA hydrogen.
4. Forth carbon / hydrogen from functional group (in this case it is OH) is called DELTA carbon and hydrogen present on alpha carbon is called DELTA hydrogen.

The reaction in which the carbonyl compound (having no alpha hydrogen) is treated with base (NaOH or KOH) to produce alcohol and Carboxylate ion is called Cannizzaro’s reaction.
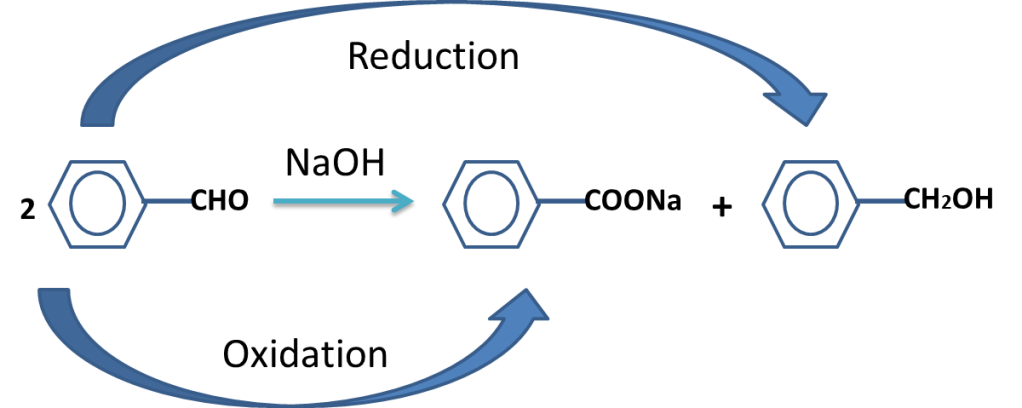
The cannizzro,s reaction is given by the aldehydes which has no alpha hydrogen.
The aldehyde oxidizes to carboxylate ion and reduced to alcohol.
Cannizzaro’s reaction is disproportionation reaction.
The reaction in which same molecule oxidizes and reduced simultaneously is called disproportionation reaction..
Question:- Which compounds gives Cannizzaro’s reaction out of the following compounds and why?
A
B


C.
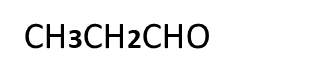
D.
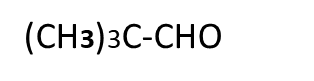
Answer:-Compounds A and C gives Cannizzaro’s reaction because they have absence of alpha hydrogen atom.
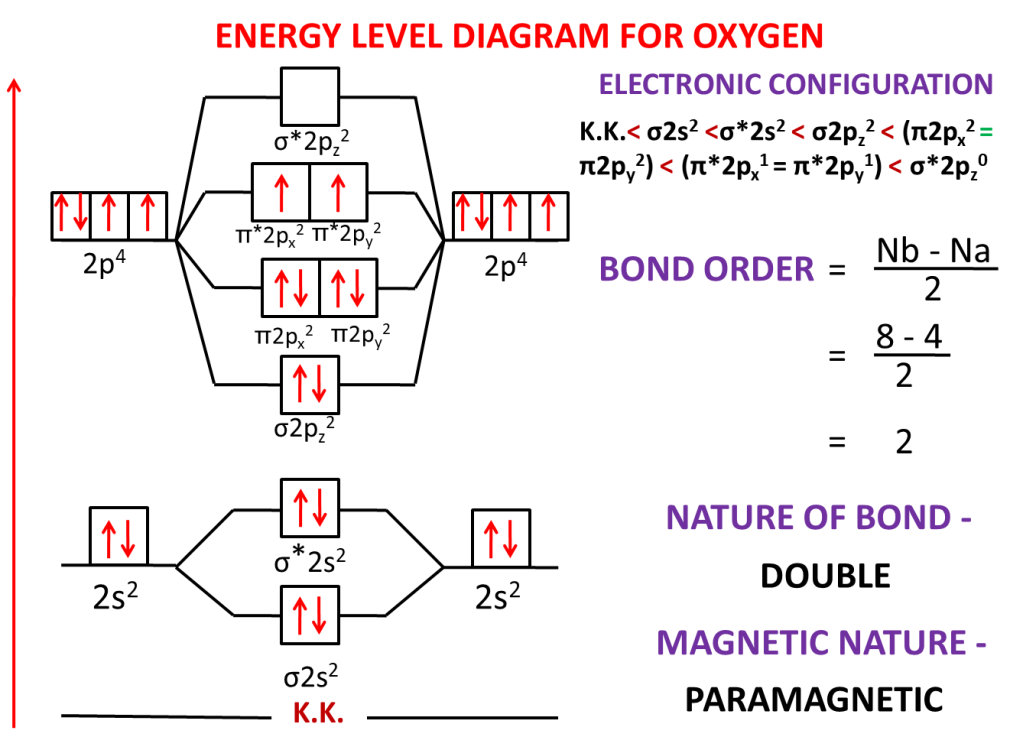
Question:-Explain the paramagnetic nature of oxygen and calculate bond order by drawing molecular orbital orbital diagram and molecular orbital electronic configuration.
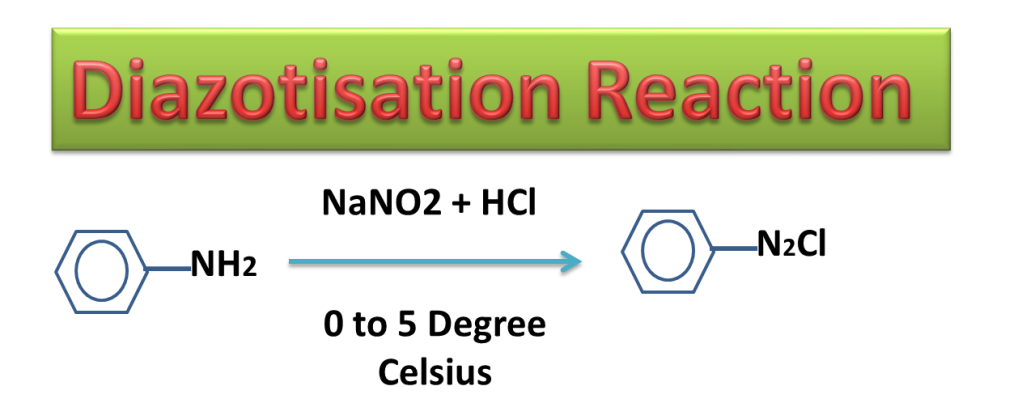
In diazotization Reaction, The aniline is treated with nitrous acid ( a mixture of sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid) at temperature 00 to 50 Celsius ( 273 K to 278 K ) to produce diazonium chloride.
Nitrous acid is produce in the reaction mixture by treating NaNO2 with HCl
NaNO2 + HCl —> HNO2 + NaCl
Diazonium salt is highly unstable and can explode at little higher temperature therefore it is prepared at lower temperature (00 to 50 Celsius).
Diazonium salt can not be separated and product mixture is used for further reaction because diazonium salt is highly unstable and explode on distillation (on heating).
Diazonium salt is very much important in organic synthesis as for preparation of large number of organic compounds, it is precursor (Reactant).
Answers are given in the end-
1. How will you distinguish butanol, butan-2-ol and 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
2. How will you distinguish aniline and phenol?
3.How will you distinguish phenol and ethanol?
4.How will you distinguish ethanamine and N-Methyl methanine.
5.How will you distinguish Propanamine and N,N-Dimethylethanamine.
6.How will you distinguish Propanamine, N-Methyethanamine and N,N-Dimethylmethanamine.
7. How will you distinguish Ethanol and Ethanoic acid.
8.How will you distinguish Methanal and Ethanal?
9.How will you distinguish Propanal and Propanol.
10.How will you distinguish Propanol and Ethanol?
11.How will you distinguish Choloromethane and Chlorobenzene.
Answer-
1.When Licas reagent (ZnCl2 + HCl ) is added than turbidity appears immediately in Methylbutan-2-ol ( tertiary alcohol), turbidity appears after 5 minutes in butan-2-ol ( Secondary alcohol) and no turbidity appears in butanol ( Primary alcohol).
2.Phenol gives violet colour with neutral FeCl3 while aniline does not.
3.Ethanol gives red colour with ceric ammonium nitrate while phenol does not.
4.Ethanamine reacts with benzenesulphonyl chloride( Hinesburg’s Reagent) which is soluble in dilute solution of NaOH, whereas N-Methyl methanine reacts but insoluble in dilute solution of NaOH.
5.Propanamine reacts with benzenesulphonyl chloride ( Hinesburg’s Reagent) which is soluble in dilute solution of NaOH, whereas N,N-Dimethylethanamine does not react.
6.Propanamine reacts with benzenesulphonyl chloride ( Hinesburg’s Reagent) which is soluble in dilute solution of NaOH whereas N-Methyl ethanine reacts but insoluble in dilute solution of NaOH whereas N,N-Dimethylethanamine does not react.
7.Ethanol gives red colour with ceric ammonium nitrate while Ethanoic acid does not.
Or Ethanol gives frutty smell of esters with ethanoic acid and few drops of conc. H2SO4 whereas ethanoic acid does not. (Note- This is ester test)
8.Ethanal gives yellow ppt with a mixture of NaOH and I2 while methanol does not ( Iodoform,s Test)
9.Propanal gives silver mirror or black ppt with Tollen,s reagent( AgNO3 + NH4OH) while Propanol does not.
Or Propanal gives red ppt with mixture of Fehling,s solution A ( solution of CuSO4) and B ( solution of sodium potassium tartarate and NaOH) while Propanol does not.
( Note- Aldehydes gives Tollens test and Fehling,s solution test while ketones does not.)
10.Ethanol gives yellow ppt with a mixture of NaOH and I2 while propanol does not (Note-This is Iodoform,s Test given by compounds having three alpha hydrogen to carbonyl group or three beta hydrogen to alcoholic group)
11.Choloromethane gives white precipitate with AgNO3 but Chlorobenzene does not.
Answers are given in the end
1.What is NFE/SHE ?
2.Explain the variation of conductivity with dilution. or How does conductivity varies with dilution ? Explain the reason for the variation ?
3.Explain the variation of molar conductivity of weak electrolyte with dilution. or How does conductivity of weak electrolyte varies with dilution ? Explain the reason for the variation ?
4.Explain the variation of molar conductivity of strong electrolyte with dilution. or How does conductivity of strong electrolyte varies with dilution ? Explain the reason for the variation ?
5.Explain Kohlrausch law
6.Calculate the Vont hoff’s factor for K4[Fe{CN)6] .
7.What is cell constant ?
8.Why can’t molar conductivity at infinite dilution of weak electrolyte be measured using graphical method ?
9.What are the secondary cells?
10. What are the fuel cells?
11.State advantages and disadvantages of fuel cells.
Answers- 1.The hydrogen electrode at 298 K with pressure of hydrogen is 1 bar and concentration of hydrogen is 1 M is called Standard Hydrogen Electrode / Normal Hydrogen Electrode. 2.Conductivity decrease with dilution because number of ions decreases per unit volume with dilution. ( Conductivity is the conductance of solution of unit volume/ one litre. 3. Molar conductivity of weak electrolyte increases with dilution due to increase in degree of dissociation. 4.Molar conductivity of strong electrolyte increases with dilution due to decrease in interionic attraction as interionic distance increase with dilution. 5.At infinite dilution molar conductivity of weak electrolyte is sum of contribution of molar conductivities of cations and anions which are independent of each other. 6. Von,t Hoff factor = 5/1 =5. 7. Cell constant is the ratio of length between vs area of electrode = L / A 8.Because line of graph never touch molar conductivity axes. 9.The cell which can be reuse again and again by charging. 10. The cell which generate energy from fuel without burning it , is called fuel cell. 11. Advantage of fuel cell-(1) It is pollution free (2) Continuous source of electricity (3) byproduct is water. Disadvantages of fuel cell- It is costly as catalysts is costly.
1. Why are transition metals ions are coloured ?
2.Transitions metals are good catalyst. Why ?
3.Transition metals form alloy. Why ?
4. Why is a dip at Mn in the graph of melting point verses atomic number ?
5. What is lanthanoid contraction ?
ANSWER-
What is d-d transition ? (From d & f block elements )
Answer:- The electronic transition between two energy levels of d orbital is called d-d transition. Movement of electron from one d orbital to other d orbital having different energy.
Where does d-d transition occur ?
Ans:- d-d transition is found in complex compounds ( or Coordination compounds ). Complex compound is made up of two entities – one is central metal atom / ion and other is Ligand (electron donor molecule or atom or ion )
Why d-d transition occur in place of simple electronic transition occurs between different shells?
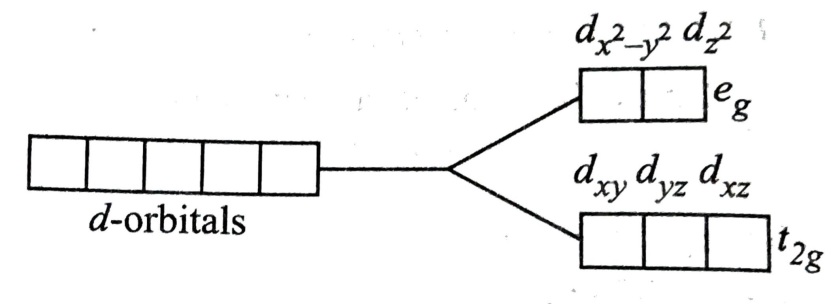
Answer:- In coordination / complex compounds d subshell containing five d orbitals split into two parts (t2g and eg ) under influence of ligand field.
In octahedral complex / coordination compounds d subshell is splited into two energy level: one is of lower energy called t2g energy level containing three d orbital dxy, dyx and dzx and other is of higher energy level called eg energy level containing two d orbitals d x2-y2 and dz2
Why complex / coordination compounds are coloured ?
In coordination / complex compound, When electron present in one of t2g orbital absorb fixed amount of energy ( absorb particular frequency or wavelength of white light ) and moves to one of eg orbital than complementary light is reflected which we see through our eyes.
e.g. CuSO4.5H2O is blue in coloured,
Sodium chromate is yellow in coloured.
Sodium dichromate is Orange in coloured
[Cu (H2O)4]2+ absorb at 600nm means Red colour and complementary colour we see is Green.
The changes for classes IX-X (2023-24) year-end Board Examinations are as under:
Particulars
Particulars Academic Session 2022-23 Academic Session 2023-24 Composition question paper year-end
examination/ Board
Examination (Theory)
Academic Session 2022-23 Competency Based Questions are 40% in the form of Multiple-Choice Questions, Case Based Questions, Source Based Integrated Questions or any other type.
Objective Questions are 20%
Remaining 40% Questions are Short Answer/ Long Answer
Questions
Academic Session 2023-24
Competency Focused Questions in the form of MCQs/Case Based Questions, Source-based Integrated Questions or any other type = 50%
Select response type
questions(MCQ) = 20%
Constructed response questions (Short Answer/ Long Answer type Questions, as per existing pattern) =30%
NEW CBSE Question Paper Pattern for 9, 10,11 & 12 Session- 2023-24
Particulars
Composition of question paper year-end examination/
Board Examination (Theory)
Academic Session 2022-23
Competency Based Questions are 30% in the form of Multiple-Choice Questions, Case Based Questions, Source Based Integrated Questions or any
other type.
Objective Question are 20%
Remaining 50% Questions
are Short Answer / Long Answer Questions
Academic Session 2023-24
Competency Focused Questions in the form of MCQs/Case Based Questions, Source-based Integrated Questions or any other type = 40%
Select response type questions (MCQ) = 20%
Constructed response questions (Short Answer Questions/Long Answer type Questions, as per existing pattern) = 40%
NEW CBSE Question Paper Pattern for 9, 10,11 & 12 Session- 2023-24
The Central Board od of secondary education, india has issued Sample Question Paper with Answer Key based on New Pattern according to Netional Education Policy 2020. The link of official page of CBSE is given below to download Question papers and Marking Scheme.
CLASS 12 ALL SUBJECTS https://cbseacademic.nic.in/SQP_CLASSXII_2022-23.html
CLASS 10 ALL SUBJECTS https://cbseacademic.nic.in/SQP_CLASSX_2022-23.html
Apply for Post of Principal, Vice Principal, PGT and TGT in Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya under Navodaya Vidyalaya Samiti ( An Autonomous Body), Department of Education, Govt. of India
1.LDCE / LDE (Notice- https://navodaya.gov.in/nvs/en/Recruitment/LDE/Notification/# )
2.Direct Recruitment ( Notice-https://navodaya.gov.in/nvs/en/Recruitment/Notification-Vacancies/)
3.Special Drive Only For North Eastern Region
( Notice-https://navodaya.gov.in/nvs/en/Recruitment/Notification-Vacancies/) ,
Using following Links- ( For all three recruitments)
https://cbseitms.nic.in/nvsrecuritment
or https://navodaya.gov.in/nvs/en/Recruitment/Fill-up-online-application/
Online Application Page https://cbseitms.nic.in/NVSRecuritment/DCExam/DCExam
http://www.chemigod/com is viewed in 91 Countries within about 1.5 years after launching
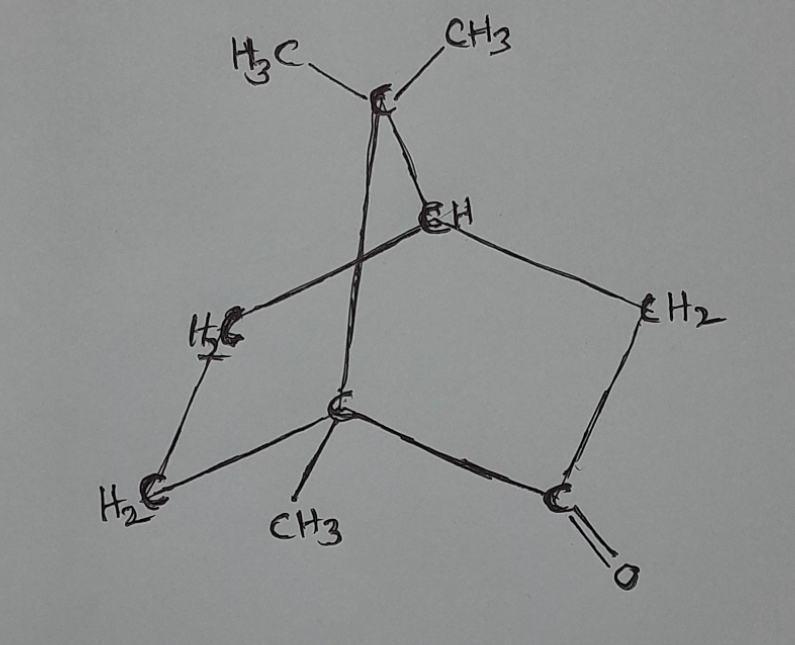
Camphor:-
Formula:-( C10H16O )
Structure:- bicyclic ketone ( Bicyclic means compounds containing two rings.)
Ketones is a functional group, in which one carbon has double bond with one oxygen and one-one single bond with other carbon atom.
Uses:-
1. It is burnt in worship.
2.As disinfectant, It produce lumps of carbon atoms which adsorb micro organism, particles of good or bad smell.
3.used on the skin as a painkiller in concentrations of 3% to 11%.
4.Camphor is used in many rub-on products to reduce pain related to cold sores, insect stings and bites, minor burns, and hemorrhoids.
5.It is used as one component of “amritdhara”
which is used to apply on forehead to relieve from headache.
6. It is used in products such as Vicks Vapo Rub.
7.Warning:-Oral camphor is unsafe. It is also important not to apply camphor to broken skin, because it can enter the body quickly and reach concentrations that are high enough to cause poisoning.
Source:-
1. Camphor is present in the volatile oils of camphor obtained from tree- Cinnamomum camphora ( Botanical Name ), or Camphor laurel
2.These days, camphor is usually manufactured from turpentine oil.
Process of making:- Camphor is obtained by using steam distillation of wood, twigs and bark of the Camphor tree, followed by purification and sublimation.
Occurrence of Camphor Tree:- In India, South east China, Taiwan, Japan, Mangolia, Indonesia.
Height:- 50- 60 feet ( 15 -18 metre )
Age :- 150 Years
Shape:- Umbrella
Width:- Up to 15 m
कपूर / या कर्पूरम :-
फॉर्मूला:- (C10H16O)
संरचना:- द्विचक्रीय कीटोन
( द्विचक्रीय वलय का अर्थ है दो वलय वाले यौगिक)
कीटोन एक कार्यात्मक समूह है, जिसमें एक कार्बन का एक ऑक्सीजन के साथ दोहरा बंधन होता है और अन्य कार्बन परमाणुओं के साथ एक-एक एकल बंधन होता है।
उपयोग:-
1. इसे पूजा में जलाया जाता है।
2. निस्संक्रामक के रूप में, यह कार्बन परमाणुओं की गांठें उत्पन्न करता है जो सूक्ष्म जीवों, अच्छी या बुरी गंध के कणों को सोख लेती हैं।
3.त्वचा पर दर्द निवारक के रूप में 3% से 11% की सांद्रता में उपयोग किया जाता है।
4.इसका उपयोग कई रगड़-उत्पादों में ठंड घावों, कीड़े के डंक और काटने, मामूली जलन और बवासीर से संबंधित दर्द को कम करने के लिए किया जाता है।
5.यह “अमृतधारा” के एक घटक के रूप में प्रयोग किया जाता है, जिसे सिर दर्द से राहत पाने के लिए माथे पर लगाने के लिए प्रयोग किया जाता है।
6. इसका उपयोग विक्स वेपो रब जैसे उत्पादों में किया जाता है।
7. चेतावनी:- मुह के द्वारा इसे लेना असुरक्षित हैI यह भी महत्वपूर्ण है कि टूटी हुई त्वचा पर कपूर न लगाएं, क्योंकि यह शरीर में जल्दी से प्रवेश कर सकता है और इतनी अधिक मात्रा में सांद्रता तक पहुँच सकता है कि विषाक्तता पैदा कर सकता है।
स्रोत:-
1.कपूर पूर्व सिनामोमम कपूर (वानस्पतिक नाम) या कपूर लॉरेल के वाष्पशील तेलों में मौजूद होता है।
2.आजकल, कपूर आमतौर पर तारपीन के तेल से बनाया जाता है।
बनाने की प्रक्रिया:-
1.कपूर की लकड़ी, टहनियों और छाल के भाप आसवन का उपयोग करके कपूर प्राप्त किया जाता है, इसके बाद शुद्धिकरण और उर्ध्वपातन किया जाता है।
कपूर के पेड़ की उपस्थिति:- भारत, दक्षिण पूर्व चीन, ताइवान, जापान, मंगोलिया, इंडोनेशिया
ऊंचाई:- 50- 60 फीट (15-18 मीटर)
आयु :- 150 वर्ष
आकार:- छाता / छतरी का आकार
चौड़ाई:- 15 मी . तक
Investigatory Project for Class 11 and 12 Chemistry and Biology CBSE Students
Aim:- To investigate the chloride content in milk.
Apparatus:- Conical flask, burette, pipettes etc.
Reagents:- Ferric alum indicator: In 10% nitric acid, prepared by boiling excess of iron alum, cooling and filtering; Potassium thiocyanate: 0.05 N, (standardized against standard potassium chloride.), Silver nitrate: Approximately 0.05 N, Concentrated nitric acid.
Theory:- The normal range of chloride content
in cow’s milk is 80-140 mg/100 ml and
in buffalo’s milk is 60-70 mg/100 ml.
Determination of chloride content in milk can be used as a means of detecting abnormal milk such as infected udders, colostrum and late lactation milk which are usually high in chloride content.
Values of chloride content higher than 0.14% (140 mg/ 100 ml) in milk indicate the presence of abnormal milk.
Estimation of chloride content in milk is based on argentometric titration (Volhard’s method). In this method a known excess quantity of standard AgNO3 solution is added to the known volume of milk. The chloride present in milk reacts with silver nitrate and forms white precipitate of insoluble silver chloride. The unused AgNO3 (which is present in excess) is back titrated against standard potassium thiocyanate (KCNS) in presence of concentrated HNO3 using ferric alum as indicator. End point of titration is the first appearance of orange-red colour which persists for at least 15 seconds. End point of titration is not clearly visible in sample titration with potassium thiocyanate (KCNS). HNO3 is added to the system to dissolve the interfering casein and also to make the solution acidic so as to keep the AgCI in the precipitated form.
Reactions:-
CI- + Ag+ —–》 AgCI
(until all Cl- is complexed)
Ag+ + SCN- ——-》 AgSCN
(to quantitate silver not complexed with chloride)
SCN- + Fe3+ —–》 FeSCN
(orange-red when there is any SCN- not complexed to Ag+)
Preparation of reagents:-
A. Potassium thiocyanate -0.05 N Solution
w = M x GMM X V ( in ml)/ 1000 w = N x GEM X V ( in ml)/ 1000
w = 0.05 N x 97 g mol- X 100 ml / 1000 = 0.485 g
Dissolve 0.485 g of in water present in 100 ml volumetric flask and make up with water up to the ring.
B. Silver nitrate: Approximately 0.05 N Solution
w = M x GMM X V ( in ml)/ 1000 w = N x GEM X V ( in ml)/ 1000
w = 0.05 N x 170 g mol- X 100 ml / 1000 = 0.85 g
Dissolve 0.85 g of in water present in 100 ml volumetric flask and make up with water up to the ring.
Procedure:-
Take 10 g of the sample, accurately weighed in a 250 ml of Erlenmeyer flask.
To this add 10 ml of silver nitrate solution and 10 ml of concentrated nitric acid. Shake the content.
Digest the mixture until reddish brown fumes are evolved.
Cool the flask and add 1 ml of saturated iron alum solution.
Determine the excess of silver nitrate by titrating with the standard potassium thiocyanate until the first appearance of an orange red colour that persists for 10 seconds.
In the same manner, determine the volume of the standard thiocyanate solution equivalent to 10 ml of silver nitrate using the same volumes of reagents and water.
| S.N. | Sample of milk | X = volume in ml of the standard potassium thiocyanate solution required by the blank | Y = volume in ml of the standard potassium thiocyanate solution required by the sample | {X- Y } | Chloride, % by weight = 0.01773 (Y – X) | Chloride as sodium chloride, % by weight = 0.02923 (Y- X) |
| 1 | Cow milk of healthy cow | |||||
| 2 | Cow milk with infected udders | |||||
| 3 | Cow milk with colostrum | |||||
| 4 | Cow milk with late lactation | |||||
| 5 | Buffalo milk of healthy Buffalo | |||||
| 6 | Cow milk with infected udders | |||||
| 7 | Cow milk with colostrum | |||||
| 8 | Cow milk with late lactation |
Calculations:-
Chloride, % by weight = 0.01773 (Y – X)
Chloride as sodium chloride, % by weight = 0.02923 (Y- X) Where,
X = volume in ml of the standard potassium thiocyanate solution required by the blank,
and
Y = volume in ml of the standard potassium thiocyanate solution required by the sample.
Resut:-The samples of milk of cow/ Buffalo with infected udders, colostrum and late lactation cases have more chloride content.
Class 12 Pre Board Question Papers 2022
with Marking Scheme / Answer Key, Biology And Accountancy
Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya
Class 10 Pre Board Question Papers 2022
with Marking Scheme / Answer Key, Science
Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya
Practical Examination Sample Question Paper 1st Term-II 2022 CBSE, India
—-‐–‐—————————————————————————————————————-
AISSCE ( CHEMISTRY PRACTICAL EXAMINATION ) 2022
Subject:- Chemistry Subject Code: – 043 Name of School :- School Code:-
Time :- 3 hours M.M. : 15
Instructions :
1.Question number 1,2 and 3 to be performed in the lab.
2.All question are compulsory.
3.Perform the given experiment and report that in examination note book systematically.
4.Use all precaution measures while working in the lab and protect your note book from chemicals, burn etc.
Questions are as follows-
Q1. Find out the molarity and strength in g/L of given unknown KMnO4 solution by using M/20 Mohr salt solution. ( Solutions of different Concentrations should be given to students, therefore prepare at least two to four of solution of KMnO4 should prepare )
AND / OR
Find out the molarity and strength in g / l of given unknown KMnO4 solution by using M/20 Oxalic Acid solution. (4)
Q2. To detect the presence of one cation and anion in given salt. (4)
Q3. Identify the functional group present in the given organic compound. (2)
Q4. Investigatory Project and viva –voice (5)
Sign of Internal Examiner ….……………… Sign of External Examiner………………………..
Name of Internal Examiner………………… Name of External Examiner………………………
Internal Examiner number ……………….. External Examine number………………………
( Note:-1.Colourless salts should be preferred . 2.Distribute salts randomly. 3.Try to give cations and anions from each group 4. Distribute organic functional groups randomly.)
Alok Sharma , PGT Chemistry
Central Board of Secondary Education ( CBSE) India, Has released Term-2 Examination Schedule for session 2021-22. It covers a lot of fraction of regular summer vacation period.
केंद्रीय माध्यमिक शिक्षा बोर्ड (सीबीएसई) भारत ने सत्र 2021-22 के लिए टर्म-2 परीक्षा कार्यक्रम जारी कर दिया है। इसमें नियमित गर्मी की छुट्टियों की अवधि के बहुत से हिस्से को शामिल किया गया है।
Grade X Term II Board Examination
27.04.22 – English
05.05.22 – Mathematics
10.05.22 – Science
14.05.22 – Social Science
18.05.22 – Hindi
Grade XII Term II Board Examination
Science Stream
02.05.22 – Hindi Core
07.05.22 – Chemistry
13.05.22 – English
20.05.22 – Physics
30.05.22 – Biology
07.06.22 – Mathematics
Grade XII Term II Board Examination
Commerce Stream
02.05.22 – Hindi Core
13.05.22 – English
17.05.22 -Business Study
23.05.22 -Accountancy
28.05.20 -Economics
07.06.22 – Mathematics
(Detection of Functional Group In given Unknown Organic Sample)
It carries 2 marks in CBSE Class 12 Science Practical Term II Examination 2021-22 session
Aim :- To detect the Functional Group In given Unknown Organic Sample.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Colour:- Colourless
State:- Liquid.
Odour:- Specific (Like Nail paint remover )
Observation Table:-
| S N | EXPERIMENT | OBSERVATION | INFERENCE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | The sample + alkaline KMnO4 solution is added drop wise to it. | Pink colour does not disappear. | Unsaturation ( Carbon-carbon double / triple bond) is not present in the sample. |
| 2. | Sample is dissolved in water and dip blue litmus paper in it or add few drops of solution on blue litmus paper with clean dropper. | No change in colour. | – OH (Phenolic) or — COOH ( Carboxylic ) functional group is absent. |
| 3. | The sample is dissolved in water and dip blue litmus paper in it or add few drops of solution on blue litmus paper with clean dropper. | No change in colour. | – NH2 ( Amine ) functional group is absent. |
| 4 | Small amount of the sample + 2,4 DNP solution + shake + (heat if required) | Yellow precipitate appears | Presence of carbonyl ( C=O ) group is confirmed. Means either aldehyde or Ketone may present. |
| 5 | Small amount of the sample +Tollen,s reagent + heat | Silver mirror ( surface of test tube becomes shiny due to deposition of silver on glass surface or black precipitate appear in test tube if silver is unable to form deposited itself on surface of test tube. | Presence of aldehyde ( -CHO ) functional group is confirmed. |
| 6 | Small amount of the sample +Mixture of Fehling solution A and B + heat | Red precipitate appears | Presence of aldehyde ( -CHO ) functional group is confirmed. |
| 7 | Small amount of the sample + Sodium nitropruside solution + add NaOH dropwise | Red colour appears | C=O (Ketone ) functional group is absent. |
Result:- The aldehyde functional group is present in the given unknown organic compound.
Medical Counselling Committee (MCC) Directorate General of health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare has been entrusted with the responsibility to hold on-line Counselling for 15% All india quota seats for UG courses. Which Link is given below-https://mcc.nic.in/WebinfoUG/Page/Page?PageId=1&LangId=
All India and State Counselling Schedule
15% अखिल भारतीय कोटा सीटों के लिए ऑनलाइन काउंसलिंग आयोजित करने की जिम्मेदारी “चिकित्सा परामर्श समिति, स्वास्थ्य सेवा महानिदेशालय, स्वास्थ्य और परिवार कल्याण मंत्रालय” को यूजी पाठ्यक्रमों के लिए सौंपी गई है। जिसका लिंक नीचे दिया गया है-https://mcc.nic.in/WebinfoUG/Page/Page?PageId=1&LangId=
अखिल भारतीय और राज्य परामर्श अनुसूची
*15% All India Quota seats MBBS/ BDS Seats of States (participation of the Union Territory of J&K is subject to their contribution of seats),
*100% MBBS/ BDS Seats of BHU,
*100% MBBS Seats of AIIMS across India,
*100% JIPMER seats ( Puducherry/ Karaikal ),
*100% AMU ( Aligarh Muslim University )
*85% of State Quota seats of DU/ I.P University (VMMC/ ABVIMS/ESIC Dental ),
*100% -Faculty of Dentistry ( Jamia Milia Islamia) along with 5% internal Quota of Jamia students
*15% IP (Insured Person) quota seats of ESIC. (Detail of Employees’ State Insurance Scheme)
15% अखिल भारतीय कोटा सीटें राज्यों की एमबीबीएस/बीडीएस सीटें (केंद्र शासित प्रदेश जम्मू-कश्मीर की भागीदारी सीटों के उनके योगदान के अधीन है),
*बीएचयू की 100% एमबीबीएस/बीडीएस सीटें,
*पूरे भारत में एम्स की 100% एमबीबीएस सीटें,
*100% जिपमर सीटें ( पुदुचेरी/कराइकल ),
*100% एएमयू (अलीगढ़ मुस्लिम विश्वविद्यालय )
*डीयू / आईपी विश्वविद्यालय (वीएमएमसी / एबीवीआईएमएस / ईएसआईसी डेंटल) की राज्य कोटा सीटों का 85%,
*100% – दंत चिकित्सा संकाय (जामिया मिल्लिया इस्लामिया) जामिया के छात्रों के 5% आंतरिक कोटा के साथ
*ESIC (कर्मचारी राज्य बीमा योजना की विस्तृत व्याख्या ) की 15% IP (बीमित व्यक्ति ) कोटा सीटें।
ऑनलाइन यूजी परामर्श (एमबीबीएस/बीडीएस/बीएससी नर्सिंग (केवल केंद्रीय नर्सिंग संस्थानों के लिए) पाठ्यक्रमों के लिए अंतिम अनुसूची ) के लिए NEET 15% AIQ/ 100% डीम्ड/केंद्रीय विश्वविद्यालय/ESIC/AFMS ( केवल पंजीकरण भाग ) और AIIMS/JIPMER (पुडुचेरी / कराइकल) सीटें शैक्षणिक वर्ष 2021 के लिए
| क्रम संख्या | संस्थान द्वारा सीट मैट्रिक्स का का सत्यापन | पंजीकरण / भुगतान | च्वाइस फिलिंग / लॉकिंग | संबंधित विश्वविद्यालय/ संस्थान द्वारा आंतरिक उम्मीदवार का सत्यापन का | सीट आवंटन का प्रसंस्करण | परिणाम | रिपोर्टिंग |
| प्रथम चरण | 17 जनवरी, 2022 से 18 जनवरी, 2022 | 19 जनवरी, 2022 से 24 तारीख जनवरी, 2022 से 12:00 बजे तक दोपहर (सर्वर समय के अनुसार) भुगतान की सुविधा होगी अपराह्न 03:00 बजे तक उपलब्ध 24 जनवरी, 2022 सर्वर समय के अनुसार | च्वाइस फिलिंग: -20 जनवरी से 24 जनवरी, 2022 (रात 11:55 बजे तक) प्रति सर्वर समय विकल्प I पसंद लॉकिंग- 24.01.2022, 04:00 अपराह्न से 24.01.2022, 11.55 (अपराह्न, सर्वर समय के अनुसार) | 25 जनवरी, 2022 से 26 जनवरी, 2022 | 27 जनवरी, 2022 से 28 जनवरी, 2022 | 29 जनवरी, 2022 | 30 जनवरी, 2022 से 04 फ़रवरी, 2022 |
| दिन | 6 दिन | 5 दिन | 2 दिन | 2 दिन | 1 दिन | 6 दिन | |
| द्वितीय चरण | 7 फरवरी, 2022 से 8 फ़रवरी, 2022 | 9 फरवरी, 2022 से 14 फरवरी, 2022 से 12:00 बजे तक दोपहर (सर्वर समय के अनुसार) भुगतान की सुविधा होगी अपराह्न 03:00 बजे तक उपलब्ध 14 फरवरी, 2022 सर्वर समय के अनुसार | च्वाइस फिलिंग: -10 फ़रवरी से 14 फ़रवरी, 2022 (रात 11:55 बजे तक) प्रति सर्वर समय विकल्प I पसंद लॉकिंग- 14.02.2022, 04:00 अपराह्न से 14.02.2022, 11.55 (अपराह्न, सर्वर समय के अनुसार) | 15 फरवरी, 2022 से 16 फरवरी, 2022 | 17 फरवरी, 2022 से 18 फरवरी, 2022 | 19 फरवरी, 2022 | 20 फरवरी, 2022 से 26 फरवरी, 2022 |
| दिन | 6 दिन | 5 दिन | 2 दिन | 2 दिन | 1 दिन | 7 दिन | |
| तृतीय चरण | 28 वें फ़रवरी, 2022 से 1 मार्च, 2022 | 2 मार्च, 2022 से 7 तारीख मार्च, 2022 (दोपहर 12 बजे) प्रति सर्वर समय) * भुगतान यह सुविधा 7 मार्च, 2022 को अपराह्न 03:00 बजे तक होगी प्रति सर्वर समय | च्वाइस फिलिंग 3 मार्च, 2022 से 7 मार्च, 2022 (रात 11:55 बजे तक) अनुसार सर्वर समय)। पसंद लॉकिंग 04:00 अपराह्न से 7 मार्च को रात 11:55 बजे तक, 2022 (सर्वर समय के अनुसार) | 8 मार्च, 2022 से 9 मार्च, 2022 | 10 मार्च, 2022 से 11 मार्च, 2022 | 12 मार्च, 2022 | 13 मार्च, 2022 से 19 मार्च, 2022 |
| दिन | 6 दिन | 5 दिन | 2 दिन | 2 दिन | 1 दिन | 7 दिन | |
| उम्मीदवारों का पंजीकरण करने के लिए डीम्ड विश्वविद्यालयों को गैर-रिपोर्टिंग और नॉन जॉइनिंग रिक्त पेड सीटों का स्थानांतरण।स्ट्रे रिक्ति में प्रवेश दौर -रिपोर्टिंग मॉड्यूल के दौरान शुरू होने वाले डीम्ड विश्वविद्यालयों के लिए |
| चतुर्थ चरण | ऑनलाइन स्ट्रे वेकेंसी राउंड के लिए निर्देश | सीट आवंटन का प्रसंस्करण | परिणाम | रिपोर्टिंग |
| i) ऑनलाइन स्ट्रे वेकेंसी राउंड के लिए कोई नया पंजीकरण / भुगतान विकल्प नहीं। ii) ऑनलाइन स्ट्रे वेकेंसी राउंड के लिए कोई नई पसंद भरने का आयोजन नहीं किया जाएगा iii) मॉप अप राउंड में उम्मीदवारों द्वारा चुने गए विकल्पों पर स्ट्रे वेकेंसी राउंड के लिए सीटों के आवंटन के लिए विचार किया जाएगा। iv) सॉफ्टवेयर चलाकर ‘ऑनलाइन’ सीटों का आवंटन v) योग्य उम्मीदवार जिनके पास कोई सीट नहीं है, वे केवल ऑनलाइन स्ट्रे वेकेंसी में भाग ले सकते हैं गोल। | 21 मार्च, 2022 | 21 मार्च, 2022 | 23 मार्च, 2022 से 26 मार्च, 2022 | |
| दिन | 1 दिन | 1 दिन | 4 दिन |
| काउंसलिंग द्वारा डीम्ड विश्वविद्यालयों को रिक्त सीटों की संख्या के दस गुना के बराबर योग्यता क्रम में छात्रों की सूची अग्रेषित करना सीट प्रोसेसिंग के बाद प्राधिकरण। (एआईक्यू/केंद्रीय विश्वविद्यालयों/एम्स/जेआईपीएमईआर (पुदुचेरी/कराइकल) उम्मीदवारों के लिए रिपोर्टिंग) और प्रवेश और 23 मार्च, 2022 से 26 मार्च, 2022 तक एक सामान्य मॉड्यूल में आयोजित किए जाने वाले डीम्ड विश्वविद्यालयों द्वारा stray रिक्ति दौर की रिपोर्टिंग |
| नोट: समय सारिणी का निष्ठापूर्वक पालन सुनिश्चित करने के लिए और परामर्श के संचालन के लिए उपलब्ध सीमित समय को ध्यान में रखते हुए, सभी भाग लेने वाले संस्थानों/महाविद्यालयों को निर्देश दिया जाता है कि वे सभी शनिवार/रविवार और राजपत्रित अवकाशों को कार्य दिवसों के रूप में मानें। |
FINAL SCHEDULE FOR ONLINE UG COUNSELING (MBBS/ BDS/ B.SC NURSING (ONLY FOR CENTRAL INSTITUTES OF NURSING) COURSES) FOR
NEET 15% AIQ/ 100% DEEMED/CENTRAL UNIVERSITIES/ESIC/AFMS (ONLY REGISTRATION PART) AND AIIMS/ JIPMER (PUDUCHERRY/ KARAIKAL) SEATS
FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2021
| SL. No. | Verification of Seat Matrix by Institutes | Registration/Payment | Choice Filling/ Locking | Verification of Internal Candidates by the respective Universities/ Institutes | Processing of Seat Allotment | Result | Reporting |
| Round-1 | 17th January, 2022 to 18th January, 2022 | 18th or19th January, 2022 to 24th January, 2022 up to 12:00 NOON ( as per Server Time) Payment facility will be available up to 03:00 PM of 24th January,2022 as per Server Time | Choice Filling: 20th January to 24th January, 2022 (up to 11:55 PM) as per Server Time Choice Locking from 04:00 PM of 24.01.2022 to 11:55 PM of 24.01.2022 as per Server Time | 25th January, 2022 to 26th January, 2022 | 27th January, 2022 to 28th January, 2022 | 29th January, 2022 | 30th January, 2022 to 4th February, 2022 |
| Days | 6 Days | 5 Days | 2 Days | 2 Days | 1 Days | 6 Days | |
| Round-2 | 7th February, 2022 to 8th February, 2022 | 9th February, 2022 to 14th February, 2022 upto12:00 NOON as per Server Time * Payment facility will be available up to 03:00 PM of 14th February, 2022 as per Server Time | Choice Filling 10th February, 2022 to 14th February, 2022 (till 11:55 PM) as per Server Time Choice Locking from 04:00 PM to 11:55 PM of 14th February, 2022, as per Server Time | 15th February, 2022 to 16th February, 2022 | 17th February, 2022 to 18th February, 2022 | 19th February, 2022 | 20th February, 2022 to 26th February, 2022 |
| Days | 6 Days | 5 Days | 2 Days | 2 Days | 1 Day | 7 Days | |
| Round-3 | 28th February, 2022 to 1st March, 2022 | 2nd March, 2022 to 7th March, 2022 (12:00 NOON as per Server Time) * Payment facility will be up to 03:00 PM of 7th March, 2022 as per Server Time | Choice Filling 3rd March, 2022 to 7th March, 2022 (till 11:55 PM) as per Server Time) Choice Locking from 04:00 PM to 11:55 PM on 7th March, 2022 as per Server Time | 8th March, 2022 to 9th March, 2022 | 10th March, 2022 to 11th March, 2022 | 12th March, 2022 | 13th March, 2022 to 19th March, 2022 |
| Days | 6 Days | 5 Days | 2 Days | 2 Days | 1 Day | 7 Days | |
| Transfer of Non Reporting & Non Joining Vacant Paid seats to Deemed Universities for carrying out Registration of candidates. Admission in Stray Vacancy Round for Deemed Universities to start during Reporting module | |||||||
| Round-3 |
| Round-4 | INSTRUCTIONS FOR ONLINE STRAY VACANCY ROUND | Processing of Seat Allotment | Result | Reporting |
| i) No New Registration/ Payment option for Online Stray Vacancy Round. ii) No Fresh Choice Filling will be conducted for Online Stray Vacancy Round iii) The Choices exercised by candidates in Mop Up Round will be considered for allotment of seats for Stray Vacancy Round iv) Allotment of seats ‘Online’ by running software v) Eligible candidates who are not holding any seat can only participate in Online Stray Vacancy Round. | 21st March, 2022 | 22nd March, 2022 | 23rd March, 2022 to 26th March, 2022 | |
| Days | 1 Day | 1 Day | 4 Days |
| Forwarding the list of students in order of merit equaling to Ten times the number of vacant seats to the Deemed Universities by the Counselling Authority after Seat Processing. Reporting for (AIQ/ Central Universities/ AIIMS/ JIPMER (Puducherry/ Karaikal) Candidates) and Admissions & Reporting for Stray Vacancy Round by Deemed Universities to be conducted in a common module from 23rd March, 2022 to 26th March, 2022 |
| Note: For ensuring faithful obedience of time schedule and also keeping in view the limited time available for conducting counselling, all participating institutes/colleges are directed to treat all Saturdays/ Sundays and Gazetted Holidays as working days. |
Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE), (India) has issued question paper and marking scheme for term 2 for class 12th and 10th you can download question paper and marking scheme by click following link of of CBSE academic website.
केंद्रीय माध्यमिक शिक्षा बोर्ड, (भारत)ने कक्षा 12वीं कक्षा 10 के लिए टर्म-2 के लिए सैंपल प्रश्न पत्र उत्तर कुंजी के साथ आज जारी कर दिए हैं। आप नीचे दिए गए लिंक पर जाकर अपने अपने विषय के प्रश्न पत्र वह उत्तर कुंजी डाउनलोड कर सकते हैं।
https://cbseacademic.nic.in/SQP_CLASSXII_2021-22.html For Class 12th
https://cbseacademic.nic.in/SQP_CLASSX_2021-22.html For Class 10th
Download Question Paper (Bilingual -English and Hindi) with Marking Scheme Class 11 Chemistry Term 1( Navodaya Vidyalaya Samiti, India ) CBSE Board.
उत्तर कुंजी के साथ प्रश्न पत्र (द्विभाषी-अंग्रेजी और हिंदी) डाउनलोड करें कक्षा 11 रसायन विज्ञान अर्धवार्षिक (नवोदय विद्यालय समिति, भारत) सीबीएसई बोर्ड I
अगर आप टेस्ट सीरीज के किसी भी टेस्ट को मिस नहीं करना चाहते हैं तो वेबसाइट को सब्सक्राइब करें।
Subscribe website if you do not want to miss any Test of Test Series.
This Google form Test includes 10 MCQ which came in the NEET ( Medical Entrance ) / IIT ( Engineering Entrance ) Examination in previous Year
Click This Link to open Google Form Test and see Result analysis immediately
The 10 questions are given below. Give the answers on the basis of following criteria.नीचे 1 प्रश्न दिए गए हैं। निम्नलिखित मानदंडों के आधार पर उत्तर दीजिए।
1.Write / Mark Answer “A”, if Both “Assertion” and “Reason” are correct statements and “Reason” is correct explanation of “Assertion”.
उत्तर “ए” लिखें/चिह्नित करें, यदि “अभिकथन” और “कारण” दोनों सही कथन हैं और “कारण” “अभिकथन” की सही व्याख्या है।
2.Write / Mark Answer “B”, if Both “Assertion” and “Reason” are correct statements and “Reason” is not correct explanation of “Assertion”.
उत्तर “बी” लिखें/चिह्नित करें, यदि “अभिकथन” और “कारण” दोनों सही कथन हैं और “कारण” “अभिकथन” की सही व्याख्या नहीं है।
3.Write / Mark Answer “C”, if “Assertion” is correct statement but “Reason” is not correct statement.
उत्तर “सी” लिखें/चिह्नित करें, यदि “अभिकथन” सही कथन है लेकिन “कारण” सही कथन नहीं है।
4.Write / Mark Answer “D”, if “Assertion” is not correct statement but “Reason” is correct statement.
उत्तर “डी” लिखें/चिह्नित करें, यदि “अभिकथन” सही कथन नहीं है लेकिन “कारण” सही कथन है।
5.Write / Mark Answer “E”, if both “Assertion” and “Reason” incorrect statements. उत्तर “ई” लिखें/चिह्नित करें, यदि दोनों “अभिकथन” और “कारण” गलत कथन हैं।
Q.1 Assertion :- A person feels happiness/ pleasure at higher altitudes.
Q.1 अभिकथन :- व्यक्ति को अधिक ऊंचाई पर सुख/सुख की अनुभूति होती है।
Reason:- At higher altitude concentration of oxygen in air becomes lower.
कारण:- अधिक ऊंचाई पर हवा में ऑक्सीजन की सांद्रता कम हो जाती है।
Q.2 Assertion :- Elevation in boiling point of 1molal solution of glucose in ethanol is higher than 1 molal solution of glucose in water.
Q.2 अभिकथन :-इथेनॉल में ग्लूकोज के 1 मोलल विलयन का क्वथनांक पानी में ग्लूकोज के 1 मोलल विलयन से अधिक होता है।
Reason:- Kb for ethanol is 1.20 K Kg /mol while Kb for water is 0.52 K Kg /mol
कारण:- इथेनॉल के लिए Kb 1.20 Kg/mol है जबकि पानी के लिए Kb 0.52 Kg/mol है I
Q.3 Assertion :- Mixing of ethanol and water leads to decrease in vapour pressure.
Q.3 अभिकथन :-इथेनॉल और पानी के मिश्रण से वाष्प के दबाव में कमी आती है।
Reason:- The intermolecular attraction decreases after mixing in case of positive deviation.
कारण:- धनात्मक विचलन की स्थिति में मिश्रण के बाद अंतराआण्विक आकर्षण कम हो जाता है।
Q.4 Assertion :- The helium is less soluble in water than hydrogen.
Q.4 अभिकथन :- हीलियम हाइड्रोजन की तुलना में पानी में कम घुलनशील है।
Reason:- K(H) for helium is more than hydrogen.
कारण:- हीलियम के लिए K(H) हाइड्रोजन से अधिक है।
Q.5 Assertion :- The molality is better than molarity.
Q.5 अभिकथन: – मोलैलिटी मोलरिटी से बेहतर है।
Reason :- Molality does not change with temperature
कारण :- तापमान के साथ मोलैलिटी नहीं बदलती है
Q.6 Assertion :- The mass percentage of solution of glucose is 10% which is prepared by mixing 5 grams of glucose in 50 gram of water.
Q.6 अभिकथन :- ग्लूकोज के घोल का द्रव्यमान प्रतिशत 10% है जो 50 ग्राम पानी में 5 ग्राम ग्लूकोज मिलाकर तैयार किया जाता है।
Reason :- Mass % is the amount of solute in grams present in 100 grams of solution.
कारण :- द्रव्यमान % 100 ग्राम घोल में मौजूद ग्राम में विलेय की मात्रा है।
Q.7 Assertion :- A solution of ethylene glycol in water is used as antifreeze mixture in radiators of vehicles at higher altitudes where temperature is sub zero.
Q.7 अभिकथन :-पानी में एथिलीन ग्लाइकॉल का एक विलयन उच्च ऊंचाई पर वाहनों के रेडिएटर्स में एंटीफ्रीज मिश्रण के रूप में उपयोग किया जाता है जहां तापमान शून्य से कम होता है।
Reason :- Mixing of ethylene glycol in water leads to depression in boiling point.
कारण:- एथिलीन ग्लाइकॉल को पानी में मिलाने से क्वथनांक में अवनमन होता है।
Q.8 Assertion :- Scuba ( deep sea) divers uses a compressed gaseous mixture of 11.7% of Helium (He), 56.2 % of Nitrogen (N2) and 32.1 % of Oxygen (O2) is used in breathing kit / cylinder.
Q.8 अभिकथन :-स्कूबा (गहरे समुद्र) के गोताखोरों में 11.7% हीलियम (He), 56.2% नाइट्रोजन (N2) और 32.1% ऑक्सीजन (O2) के संपीडित गैसीय मिश्रण का उपयोग श्वास किट/सिलेंडर में किया जाता है।
Reason:- The above compressed gaseous mixture protects scuba divers from painful effect of “bends”.
कारण:- उपरोक्त संपीड़ित गैसीय मिश्रण स्कूबा गोताखोरों को “दर्दनाक बीमारी” के दर्दनाक प्रभाव से बचाता है।
Q.9 Assertion :- Ice on the road is melted by sprinkling salt on the ice.
Q.9 अभिकथन :-बर्फ पर नमक छिड़कने से सड़क की बर्फ पिघल जाती है।
Reason:- Addition of salt decreases the melting point of ice and melting point go down than temperature of environment.
कारण:- नमक मिलाने से बर्फ का गलनांक कम हो जाता है और गलनांक पर्यावरण के तापमान से नीचे चला जाता है।
Q.10 Assertion :- Addition of ethanol in water increases the partial pressure of solution.
Q.10 अभिकथन :-पानी में एथेनॉल मिलाने से विलयन का आंशिक दाब बढ़ जाता है।
Reason:- According to Raoult’s law, the vapour pressure of components of solution is directly proportional to their mole fraction in solution.
कारण:- राउल्ट के नियम के अनुसार विलयन के घटकों का वाष्प दाब विलयन में उनके मोल अंश के समानुपाती होता है।
Answer:-
| 1-D | 2-A | 3-D | 4-C | 5-A | 6-D | 7-C | 8-A | 9-A | 10-B |
Q-1: A person feels vomiting, nausea and problem in thinking and experience dearth at higher altitudes which is called anoxia and it is due to lack of concentration of oxygen at higher altitudes, Therefore the assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct
अधिक ऊंचाई पर व्यक्ति को उल्टी, मिचली और सोचने में समस्या महसूस होती है और उसकी मृत्यु हो सकती है, जिसे एनोक्सिया कहा जाता है और यह अधिक ऊंचाई पर ऑक्सीजन की एकाग्रता की कमी के कारण होता है।
Q-2- Elevation in boiling point =Kb X m
Here molalities of both solutions is same therefore elevation in boiling point will depend on value of Kb ie molal elevation constant or ebulioscopic constant of solvent which is higher for ethanol solvent.
इथेनॉल में ग्लूकोज के 1molal घोल के क्वथनांक में ऊंचाई पानी में ग्लूकोज के 1 molal घोल से अधिक है क्योंकि इथेनॉल के लिए Kb (1.20 Kg /mol) पानी के लिए Kb (0.52 Kg / mol ) से अधिक है
क्वथनांक में वृद्धि / उन्नयन = Kb X m
यहां दोनों विलयनों की मोलैलिटी समान है इसलिए क्वथनांक में उन्नयन Kb के मान पर निर्भर करेगा अर्थात मोलल उन्नयन स्थिरांक या विलायक का एबुलियोस्कोपिक स्थिरांक जो इथेनॉल विलायक के लिए अधिक होता है।
Q-3-Mixing of ethanol and water leads to increase in vapour pressure because
The intermolecular attraction forces among among the water and ethanol molecules are less than intermolecular forces among the water molecules in pure water and intermolecular attraction forces among the ethanol molecules in pure ethanol, causes positive deviation. Means intermolecular attraction forces decreases after mixing and more vapours will be produced will create more vapour pressure.
A-A or B-B > A-B
इथेनॉल और पानी के मिश्रण से वाष्प के दबाव में वृद्धि होती है क्योंकि पानी और इथेनॉल अणुओं के बीच अंतर-आणविक आकर्षण बल शुद्ध पानी में पानी के अणुओं के बीच अंतर-आणविक बल और शुद्ध इथेनॉल में इथेनॉल अणुओं के बीच अंतर-आणविक आकर्षण बल से कम होते हैं, जो सकारात्मक विचलन का कारण बनते हैं। मतलब इंटरमॉलिक्युलर आकर्षण बल मिश्रण के बाद कम हो जाते हैं और अधिक वाष्प उत्पन्न होंगे और अधिक वाष्प दबाव पैदा करेंगे।
A-A or B-B > A-B
Q-4-The helium is less soluble in water than hydrogen because K(H) for helium is less than hydrogen.
According to henery’s law :- m = K(H) X
mass of gas in solution = Henery law constant x Mole fraction
Therefore a gas having more K(H) value will be more soluble in water.
The gas having higher value of K(H) is more polar and we know more polar solute will be more soluble in polar solvent i.e. water.
हीलियम हाइड्रोजन की तुलना में पानी में कम घुलनशील है क्योंकि हीलियम के लिए K(H) हाइड्रोजन से कम है।
हेनरी के नियम के अनुसार :- m = K(H) X
विलयन में गैस का द्रव्यमान = हेनरी नियम स्थिरांक x मोल अंश
इसलिए अधिक K(H) मान वाली गैस पानी में अधिक घुलनशील होगी।
K(H) के उच्च मान वाली गैस अधिक ध्रुवीय होती है और हम जानते हैं कि अधिक ध्रुवीय विलेय ध्रुवीय विलायक यानी पानी में अधिक घुलनशील होगा।
Q-5- The molality is better than molarity because Molality does not change with temperature.(
Molarity) M = W(B) / GMM (B) x V (in Liter)
Here V i.e. volume of solution is used which affect with with temperature and thereby alter the molarity (M)
(Molality) m = W(B) / GMM (B) x W(A) (in Kilogram)
Here weight of solvent is used which does not affect with temperature and thus molality (m) remains unaffected.
मोलरिटी मोलरिटी से बेहतर है क्योंकि मोलिटी तापमान के साथ नहीं बदलती है।
(मोलरिटी) M = W(B) / GMM (B) x V(लीटर में)
यहाँ V यानि विलयन के आयतन का उपयोग किया जाता है जो तापमान के साथ प्रभावित होता है और इस तरह मोलरिटी (M) को बदल देता है।
(मोललिटी) m = W(B) / GMM (B) x W(A) (किलोग्राम में)
यहाँ विलायक के भार का उपयोग किया जाता है जो तापमान से प्रभावित नहीं होता है और इस प्रकार मोललिटी (m) अप्रभावित रहता है।
Q-6-Mass % is the amount of solute in grams present in 100 grams of solution.
द्रव्यमान % 100 ग्राम घोल में मौजूद ग्राम में विलेय की मात्रा है।
Mass % = W(B) x 100 / W
Mass % = W(B) x 100 / ( W(A) +W (B)
Mass % = 5 g x 100 / ( 50 g + 5 g )
Mass % = =500 / 55
Mass % = 9.09%
Therefore Assertion is wrong but reason is correct.
अतः अभिकथन गलत है परन्तु कारण सही है I
Q-7- Mixing of ethylene glycol in water leads to depression in freezing ( not in boiling point ) point because addition of solute in water decreases freezing point. If temperature of environment is -8 degree Celsius than water in radiator of vehicle will freeze but if water is mixed with sufficient amount of ethylene glycol than freezing point becomes lower than -8 degree Celsius, say -10 degree Celsius than water will not freeze at -8 degree Celsius.
एथिलीन ग्लाइकॉल को पानी में मिलाने से हिमांक में कमी आती है क्योंकि पानी में विलेय मिलाने से हिमांक कम हो जाता है। यदि पर्यावरण का तापमान -8 डिग्री सेल्सियस है, तो वाहन के रेडिएटर में पानी जम जाएगा, लेकिन अगर पानी में पर्याप्त मात्रा में एथिलीन ग्लाइकॉल मिला दिया जाए तो हिमांक -8 डिग्री सेल्सियस से कम हो जाता है, मान लीजिए-10 डिग्री सेल्सियस हो जाता हैतो -8 डिग्री सेल्सियस पर पानी नहीं जमेगा।
Q-8-Scuba ( deep sea) divers uses a compressed gaseous mixture of 11.7% of Helium (He), 56.2 % of Nitrogen (N2) and 32.1 % of Oxygen (O2) is used in breathing kit / cylinder,
WHEREAS the percentage of nitrogen is 78% in atmosphere.
When scuba diver go deep inside the sea the nitrogen dissolve in blood with oxygen gas but oxygen is absorbed by cells and utilized but nitrogen remain insoluble in blood. When scuba diver comes up fast than this dissolved nitrogen comes out of blood in the form of small bubbles and these bubbles of nitrogen causes hindrance in the movement of blood in the capillaries. This situation is called “bends” and creates a lot of pain in body and muscles and it may cause death by drowning.
Therefore Helium gas is mixed to reduce percentage of nitrogen and helium gas is almost insoluble in blood. With this mixture a scuba diver comes up slowly from deep sea which helps also.
स्कूबा (गहरा समुद्र) के गोताखोर 11.7% हीलियम (He), 56.2% नाइट्रोजन (N2) और 32.1% ऑक्सीजन (O2) के संपीडित गैसीय मिश्रण का उपयोग श्वास किट/सिलेंडर में करते हैं,
जबकि वायुमंडल में नाइट्रोजन का प्रतिशत 78% है।
जब स्कूबा डाइवर समुद्र के अंदर गहराई तक जाता है तो नाइट्रोजन ऑक्सीजन गैस के साथ रक्त में घुल जाता है लेकिन ऑक्सीजन कोशिकाओं द्वारा अवशोषित हो जाती है और उपयोग की जाती है लेकिन नाइट्रोजन रक्त में अघुलनशील रहती है। जब स्कूबा डाइवर तेजी से ऊपर आता है तो यह घुली हुई नाइट्रोजन रक्त से छोटे-छोटे बुलबुलों के रूप में बाहर आती है और नाइट्रोजन के ये बुलबुले केशिकाओं में रक्त की गति में बाधा उत्पन्न करते हैं। इस स्थिति को “बेंड” कहा जाता है और शरीर और मांसपेशियों में बहुत दर्द होता है और यह डूबने से मृत्यु का कारण बन सकता है।
इसलिए नाइट्रोजन के प्रतिशत को कम करने के लिए हीलियम गैस मिलाया जाता है और हीलियम गैस रक्त में लगभग अघुलनशील होती है। गहरे समुद्र से स्कूबा डाइवर की धीमी गति से धीरे-धीरे ऊपर आने में भी इस परशानी मदद मिलती है।I
Q-9-Depression in freezing point =Kf x m where Kf is cryoscopic constant or molal depression constant.
Depression in freezing point =Kf x W(B) / GMM(B) x W(A)
Addition of solute [ W(B) ] decrease the freezing point of water and water remains liquid above freezing point.
Suppose the temperature of environment or particular location is -5 degree Celsius and after addition od salt in ice make freezing point of water -7 degree Celsius in spite of zero degree Celsius. Now water or more precisely salt solution of water remain liquid above -7 degree Celsius and turns into ice below -7 degree Celsius, But the temperature of road or location is – 5 degree Celsius, therefore, water should be in liquid form and ice will melt on adding salt to it.
हिमांक में अवनमन = Kf x m जहां Kf क्रायोस्कोपिक स्थिरांक या मोलल अवनमन स्थिरांक है।
हिमांक में अवनमन = Kf x W(B) / GMM(B) x W(A)
विलेय [W(B)] मिलाने से पानी का हिमांक कम हो जाता है और पानी हिमांक से ऊपर तरल रहता है।
मान लीजिए पर्यावरण या सड़क या विशेष स्थान का तापमान -5 डिग्री सेल्सियस है और बर्फ में नमक मिलाने के बाद शून्य डिग्री सेल्सियस के बजाये पानी का हिमांक -7 डिग्री सेल्सियस हो जाता है।
अब पानी या अधिक सटीक रूप से कहो तो पानी का नमक घोल -7 डिग्री सेल्सियस से ऊपर तरल रहता है और -7 डिग्री सेल्सियस से नीचे बर्फ में बदल जाता है,
लेकिन सड़क या स्थान का तापमान – 5 डिग्री सेल्सियस होता है, इसलिए पानी तरल रूप में होना चाहिए और बर्फ में नमक मिलाने पर यह घोल / विलियन में पिघल जाएगी।
Q-10- Both statements are correct but there is no relationship between assertion and reason. By mixing any solute in water, vapour pressure may decrease due to attraction forces among two species decreases after mixing as compared to attraction forces in pure state.
दोनों कथन सही हैं लेकिन कथन और कारण के बीच कोई संबंध नहीं है। किसी भी विलेय को पानी में मिलाने से, शुद्ध अवस्था में आकर्षण बलों की तुलना में दो तरल पदार्थों के बीच आकर्षण बल कम होने के कारण घोल का वाष्प दाब कम हो सकता है।

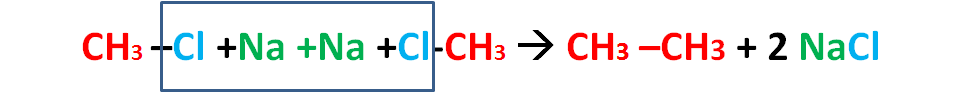
The WURTZ REACTION was named after Charles Adolphe Wurtz. Wurtz reaction is a coupling reaction in organic chemistry, organometallic chemistry and inorganic chemistry. वुर्टज अभिक्रिया का नाम चार्ल्स एडॉल्फ वुर्टज के नाम पर रखा गया था। वुर्टज अभिक्रिया अभिक्रिया कार्बनिक रसायन विज्ञान, कार्ब धात्विक (ऑर्गोमेटेलिक) रसायन विज्ञान और अकार्बनिक रसायन विज्ञान में एक युग्मन अभिक्रिया है।
In Wurtz reaction two alkyl halides are reacted with sodium metal in dry ether solution to form a higher alkane. In this reaction alkyl halides are treated with sodium metal in dry ethereal (free from moisture) solution to produce higher alkanes. WURTZ REACTION is used for the preparation of higher alkanes containing even number of carbon atoms. वुर्ट्ज अभिक्रिया में दो ऐल्किल हैलाइडों को सोडियम धातु के साथ शुष्क ईथर विलयन में अभिक्रिया करके एक उच्च ऐल्केन बनाया जाता है। इस अभिक्रिया में ऐल्किल हैलाइडों को सोडियम धातु के साथ शुष्क ईथर (नमी से मुक्त) विलयन में उपचारित किया जाता है ताकि उच्च ऐल्केन प्राप्त हो सकें। वुर्ट्ज अभिक्रिया का उपयोग कार्बन परमाणुओं की सम संख्या वाले उच्च एल्केन्स की तैयारी के लिए किया जाता हैI
Advanced Knowledge:- Other metals for example silver, zinc, iron, activated copper, indium and a mixture of manganese and copper chloride have also been used in the Wurtz coupling reaction. उच्च ज्ञान:- अन्य धातुओं जैसे चांदी, जस्ता, लोहा, सक्रिय तांबा, इंडियम और ( मैंगनीज और तांबा क्लोराइड का मिश्रण) भी वर्टज़ युग्मन अभिक्रिया में उपयोग किया जाता है।
A coupling reaction is that where two fragments of two molecules are joined together with the help of a metal catalyst. युग्मन अभिक्रिया वह होती है जिसमें दो अणुओं के दो टुकड़े एक धातु उत्प्रेरक की सहायता से आपस में जुड़ जाते हैं।


The reaction consists of a metal–halogen exchange involving the radical species R· (as in the formation of a Grignard reagent) with formation of carbon–carbon bond. प्रतिक्रिया में एक धातु-हैलोजन विनिमय होता है जिसमें कार्बन-कार्बन बंधन के गठन के साथ एल्काइल मुक्त रेडिकल प्रजाति
(R ·) शामिल होता है। (जैसा कि ग्रिग्नार्ड अभिकर्मक के निर्माण में होता है)
Step-1 :- One electron from the metal is transferred to the halogen to produce a metal halide and an alkyl radical.
चरण -1:- धातु से एक इलेक्ट्रॉन को हलोजन में स्थानांतरित करके एक धातु हैलाइड और एक अल्काइल रेडिकल का उत्पादन किया जाता है।
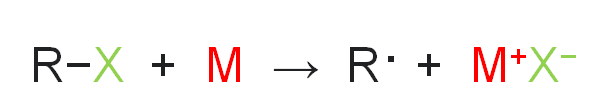
Step-2:- Now the alkyl radical accepts an electron from another metal atom to form an alkyl anion ( Carbanion).
चरण -2:-अब अल्काइल रेडिकल एक अन्य धातु परमाणु से एक इलेक्ट्रॉन को एक अल्काइल आयन (कार्बनियन) बनाने के लिए स्वीकार करता है।
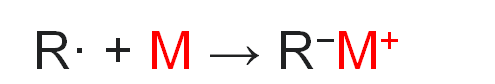
Step-3:-In last step, the nucleophilic carbon of the alkyl anion displaces the halide in an SN2 reaction, forming a new carbon–carbon covalent bond.
चरण -3:-अंतिम चरण में, एल्काइल आयन का न्यूक्लियोफिलिक कार्बन SN2 प्रतिक्रिया में हैलाइड को विस्थापित करता है, जिससे एक नया कार्बन-कार्बन सहसंयोजक बंधन बनता है।
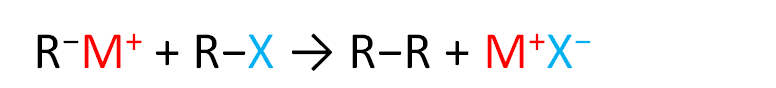
Comparison of these three reaction:- इन तीनों अभिक्रियाओं की तुलना:-
Wurtz’s Reaction
R-X +Na + Na X-R –> R-R +Na X
R = Alkyl Group (e.g. CH3-, C2H5– ….)
Ph = Phenyl ( C6H5-)
Wurtz’s Reaction
Ph-X + Na + Na + X-R –> Ph-R + NaX
Wurtz-Fittig’s Reaction
Ph-X + Na + Na + X-Ph –> Ph-Ph + NaX
Advantage of Wurtz Reaction:- Wurtz coupling is useful in closing small, ( especially three-membered) rings. e.g. -Bicyclobutane was prepared this way from 1-bromo-3-chlorocyclobutane in 95% yield. वुर्टज अभिक्रिया का लाभ:- वुर्टज युग्मन छोटे, (विशेष रूप से तीन-सदस्यीय) रिंगों को बंद करने में उपयोगी है। जैसे 1-ब्रोमो-3-क्लोरोसाइक्लोब्यूटेन से 95% उपज में इस तरह से बाइसाइक्लोब्यूटेन तैयार किया गया था।
Limitations of the Wurtz reaction:-
1.Wurtz reaction is not used generally used because of side reactions. It has limited use to the synthesis of symmetric alkanes.
आमतौर पर साइड रिएक्शन के कारण वुर्टज अभिक्रिया का उपयोग नहीं किया जाता है। सममित अल्केन्स के संश्लेषण के लिए इसका सीमित उपयोग है।
2.If two dissimilar alkyl halides are taken as reactants, then the product is a mixture of alkanes that is often difficult to separate by fractional distillation as the differences between the boiling points of the products are very low.
यदि दो असमान ऐल्किल हैलाइडों को अभिकारकों के रूप में लिया जाता है, तो उत्पाद ऐल्केनों का मिश्रण होता है जिसे भिन्नात्मक आसवन द्वारा अलग करना प्रायः कठिन होता है क्योंकि उत्पादों के क्वथनांकों के बीच का अंतर बहुत कम होता है।
3.Wurtz reaction fails in case of tertiary halides.
तृतीयक हैलाइड के मामले में वुर्टज अभिक्रिया विफल हो जाती है।
4.Methane can not be obtained by this method.
इस विधि से मीथेन प्राप्त नहीं किया जा सकता है।
5.A side reaction occurs to produce an alkene due to involvement of free radical species. This side reaction becomes more significant when the alkyl halides are bulky at the halogen-attached carbon atom.
मुक्त मूलक प्रजातियों की भागीदारी के कारण, एक ऐल्कीन उत्पन्न करने के लिए एक पार्श्व अभिक्रिया होती है। यह पार्श्व अभिक्रिया तब और अधिक महत्वपूर्ण हो जाती है जब हैलोजन-संलग्न कार्बन परमाणु पर ऐल्किल हैलाइड भारी होते हैं।
6.Wurtz reaction has poor yield which is a consequence of multiple product formation. In the case of 1,3-dihalides, 1,4-dihalides, 1,5-dihalides, 1,6- dihalides, it leads to formation of cyclic products. In case of vicinal dihalides, alkenes are formed, whereas alkynes are formed in geminal dihalides.
वुर्टज अभिक्रिया में मुख्य उत्पाद बहुत कम मात्रा में बनता है जो कई-उत्पाद निर्माण का परिणाम है। 1,3-डाइहैलाइड, 1,4-डाइहैलाइड, 1,5डाइहैलाइड, 1,6-डाइहैलाइड के मामले में, यह चक्रीय उत्पादों के निर्माण की ओर जाता है। विसिनल डाइहैलाइड में ऐल्कीन बनते हैं, जबकि ऐल्काइन जेमिनल डाइहैलाइड में बनते हैं।
CLICK HERE TO GIVE QUIZ THROUGH GOOGLE FORM This quiz Contains solutions of questions also as feedback and numerical problems. This quiz includes Bohr’s model of an atom , Quantum mechanical model of an atom, Heisenberg’s principal, Plank’s Equation, Photoelectric effect, Dual nature of EMR and Electron, Quantum numbers etc.
NOTE : – If you are unable to open this link in mobile than try desktop view in your mobile. There are two ways
1. If you are viewing a round shaped symbol of earth than click it
2. Go to three dots on the right upper corner of your mobile and select desktop view from drop down list.
Central Board of Secondary Education, INDIA, issued sample questions with answer key for Class 10 session 2021-22. Click the following links of CBSE to download. Click on SQP for Sample Question Paper and Click on MS for Marking Scheme. केंद्रीय माध्यमिक शिक्षा बोर्ड ने सत्र 2021-22 के लिए कक्षा 10 की उत्तर कुंजी के साथ नमूना प्रश्न जारी किए। डाउनलोड करने के लिए सीबीएसई के निम्नलिखित लिंक पर क्लिक करें। सैंपल प्रश्न पत्र के लिए SQP पर क्लिक करें और मार्किंग स्कीम के लिए MS पर क्लिक करें।
| Subject | Sample Question Paper | Marking Scheme |
|---|---|---|
| Science | SQP | MS |
| Elements of Book Keeping and Accountancy | SQP | MS |
| Elements of Business | SQP | MS |
| English (Language & Literature) | SQP | MS |
| Hindi A | SQP | MS |
| Hindi B | SQP | MS |
| Home Science | SQP | MS |
| Computer Application | SQP | MS |
| Mathematics (Basic) | SQP | MS |
| Mathematics (Standard) | SQP | MS |
| Social Science | SQP | MS |
| NCC | SQP | MS |
| Hindustani Music (Melodic) | SQP | MS |
| Hindustani Music (Percussion) | SQP | MS |
| Hindustani Music (Vocal) | SQP | MS |
| Carnatic Music-Melodic Instruments | SQP | MS |
| Carnatic Music-Percussion Instruments | SQP | MS |
| Carnatic Music-Vocal | SQP | MS |
| Painting | SQP | MS |
| Arabic | SQP | MS |
| Bengali | SQP | MS |
| Assamese | SQP | MS |
| Bahasa Melayu | SQP | MS |
| Bhutia | SQP | MS |
| Bodo | SQP | MS |
| French | SQP | MS |
| German | SQP | MS |
| Gujarati | SQP | MS |
| Gurung | SQP | MS |
| Japanese | SQP | MS |
| Kannada | SQP | MS |
| Kashmiri | SQP | MS |
| Lepcha | SQP | MS |
| Limboo | SQP | MS |
| Malayalam | SQP | MS |
| Manipuri | SQP | MS |
| Mizo | SQP | MS |
| Marathi | SQP | MS |
| Nepali | SQP | MS |
| Odia | SQP | MS |
| Persian | SQP | MS |
| Punjabi | SQP | MS |
| Rai Language | SQP | MS |
| Russian | SQP | MS |
| Sanskrit | SQP | MS |
| Sherpa | SQP | MS |
| Sindhi | SQP | MS |
| Spanish | SQP | MS |
| Tamil | SQP | MS |
| Tamang | SQP | MS |
| Tangkhul | SQP | MS |
| Telugu AP | SQP | MS |
| Telugu Telangana | SQP | MS |
| Thai | SQP | MS |
| Tibetan | SQP | MS |
| Urdu A | SQP | MS |
| Urdu B | SQP | MS |
Central Board of Secondary Education, INDIA, issued sample questions with answer key for Class 12 for session 2021-22. Click the following links of CBSE to download. Click on SQP for Sample Question Paper and Click on MS for Marking Scheme. केंद्रीय माध्यमिक शिक्षा बोर्ड ने सत्र 2021-22 के लिए कक्षा 12 की उत्तर कुंजी के साथ नमूना प्रश्न जारी किए। डाउनलोड करने के लिए सीबीएसई के निम्नलिखित लिंक पर क्लिक करें। सैंपल प्रश्न पत्र के लिए SQP पर क्लिक करें और मार्किंग स्कीम के लिए MS पर क्लिक करें।
| Accountancy | SQP | MS |
| Arabic | SQP | MS |
| Assamese | SQP | MS |
| Bengali | SQP | MS |
| Bhutia | SQP | MS |
| Biology | SQP | MS |
| Biotechnology | SQP | MS |
| Bodo | SQP | MS |
| Business Studies | SQP | MS |
| Carnatic Melodic | SQP | MS |
| Carnatic Percussion | SQP | MS |
| Carnatic Vocal | SQP | MS |
| Commercial Art | SQP | MS |
| Chemistry | SQP | MS |
| Computer Science | SQP | MS |
| Dance Manipuri | SQP | MS |
| Economics | SQP | MS |
| Engg. Graphic | SQP | MS |
| English Core | SQP | MS |
| English Elective | SQP | MS |
| Entrepreneurship | SQP | MS |
| French | SQP | MS |
| Geography | SQP | MS |
| German | SQP | MS |
| Gujarati | SQP | MS |
| Hindi Elective | SQP | MS |
| Hindi Core | SQP | MS |
| History | SQP | MS |
| Hindustani Music (Melodic) | SQP | MS |
| Hindustani Music (Percussion) | SQP | MS |
| Hindustani Music (Vocal) | SQP | MS |
| Home Science | SQP | MS |
| Informatics Practices | SQP | MS |
| Japanese | SQP | MS |
| Kannada | SQP | MS |
| Kashmiri | SQP | MS |
| Kathak | SQP | MS |
| Kathakali | SQP | MS |
| Kuchipudi | SQP | MS |
| Legal Studies | SQP | MS |
| Lepcha | SQP | MS |
| Limboo | SQP | MS |
| Malayalam | SQP | MS |
| Manipuri | SQP | MS |
| Marathi | SQP | MS |
| Applied Mathematics | SQP | MS |
| Mathematics | SQP | MS |
| Mizo | SQP | MS |
| NCC | SQP | MS |
| Nepali | SQP | MS |
| KTPI | SQP | MS |
| Odia | SQP | MS |
| Painting | SQP | MS |
| Graphic | SQP | MS |
| Sculpture | SQP | MS |
| Persian | SQP | MS |
| Physical Education | SQP | MS |
| Physics | SQP | MS |
| Political Science | SQP | MS |
| Psychology | SQP | MS |
| Punjabi | SQP | MS |
| Russian | SQP | MS |
| Sindhi | SQP | MS |
| Science | SQP | MS |
| Sociology | SQP | MS |
| Spanish | SQP | MS |
| Sanskrit Core | SQP | MS |
| Sanskrit Elective | SQP | MS |
| Tamil | SQP | MS |
| Tangkhul | SQP | MS |
| Telugu (AP) | SQP | MS |
| Telugu (Telangana) | SQP | MS |
| Tibetan | SQP | MS |
| Urdu Core | SQP | MS |
| Urdu Elective | SQP | MS |
Click on following link to give test through google form –> CLICK TO START QUIZ प्रश्नोत्तरी शुरू करने के लिए यहां क्लिक करें I
Highly useful for NEET, IIT JEE, Other competitive exam, class 12 and graduation (B.Sc.) students.एनईईटी, आईआईटी जेईई, अन्य प्रतियोगी परीक्षाओं, कक्षा 12 और स्नातक (B.Sc.) के छात्रों के लिए अत्यधिक उपयोगी।
This quiz not only test but also useful for effective learning the concepts and repeated test will improve your deep learning. It is basis to learn SN1 and SN2 reaction mechanism in haloalkanes and other similar reactions. Comment / give feedback me to prepare and improve more Quiz . Comment box is given below—यह प्रश्नोत्तरी न केवल परीक्षण बल्कि अवधारणाओं को प्रभावी ढंग से सीखने के लिए भी उपयोगी हैI बार-बार परीक्षण आपके सीखने में गहराई से सुधार करेगा।यह हेलोऐल्केन और अन्य समान अभिक्रियाओ में SN1 और SN2 अभिक्रिया की क्रियाविधि को सीखने का आधार है।
Attempt this quiz from NCERT book (INDIA), Unit -1 of Class/ Standard 11, This quiz contains PISA / Case Study like 20 questions. CLICK HERE TO GIVE QUIZ on GOGLE FOORM This Quiz is useful for all classes and Chemistry / Science Lovers.
The pattern of question paper of NEET / All India Medical Entrance Examination 2021 has been changed. The details are as follows-
नीट/अखिल भारतीय मेडिकल प्रवेश परीक्षा 2021 के प्रश्न पत्र के पैटर्न में बदलाव किया गया है। विवरण निम्नानुसार हैं-
The Test pattern of NEET (UG)-2021 comprises of two Sections. Each subject will consist of two
sections. Section A will consist of 35 Questions and Section B will have 15 questions, out of
these 15 Questions, candidates can choose to attempt any 10 Questions. So, the total number
of questions and utilization of time will remain the same.
The pattern
टेस्ट का पैटर्न:- NEET (UG)-2021 के टेस्ट पैटर्न में दो खंड शामिल हैं। प्रत्येक विषय में दो शामिल होंगे
खंड। सेक्शन ए में 35 प्रश्न होंगे और सेक्शन बी में 15 में से 15 प्रश्न होंगे I 15 प्रश्नो में से उम्मीदवार को किसी भी 10 प्रश्नों को करना हैं।अत: कुल प्रश्न संख्या और समय सीमा वही रहेगी l
सत्र 2021-22 में प्रवेश के लिए NEET (UG)-2021 परीक्षा का पैटर्न इस प्रकार है:–
| Serial Number क्रम संख्या | Subject विषय | Section (s) अनुभाग | Number of question(s) प्रश्नों की संख्या | Marks Each question carries 4 marks (अंक) प्रत्येक सवाल 4 अंक रखता है | Types of questions प्रश्नों के प्रकार |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Physics | A B | 35 15 | 140 40 | MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions). सभी बहुविकल्पी प्रश्न हैं |
| 2 | Chemistry | A B | 35 15 | 140 40 | -SAME- |
| 3 | Zoology | A B | 35 15 | 140 40 | -SAME- |
| 4 | Botany | A B | 35 15 | 140 40 | -SAME- |
Note: Correct option marked will be given (4) marks and Incorrect option marked will be minus one (-1) mark.
Unattempted/Unanswered Questions will be given no marks.
नोट: चिह्नित सही विकल्प को (4) अंक दिया जाएगा और गलत विकल्प के रूप में चिह्नित किया गया माइनस एक (-1) अंक होगा।
अनुत्तरित / अनुत्तरित प्रश्नों को कोई अंक नहीं दिया जाएगा।
The important points to note:
I. Each question carries 04 (four) marks and, for each correct answer candidate will get 04 (four) marks.
II. For each incorrect answer, 01(one) mark will be deducted from the total score.
III. To answer a question, the candidate has to find, for each question, the correct answer/ best option.
IV. However, after the process of the challenge of key, if more than one option is found to be correct then all/any
one of the multiple correct/best options marked will be given four marks (+4).
Any incorrect option marked will be given minus one mark (-1).
Unanswered/Unattempted questions will be given no marks.
In case, a question is dropped/ ignored, all candidates will be given four marks (+4) irrespective of the fact whether the question has been attempted or not attempted by the candidate.
ध्यान देने योग्य महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु:
I. प्रत्येक प्रश्न में 04 (चार) अंक हैं और प्रत्येक सही उत्तर के लिए उम्मीदवार को 04 (चार) अंक मिलेंगे।
द्वितीय. प्रत्येक गलत उत्तर के लिए, कुल अंक से 01 (एक) अंक काट लिया जाएगा।
III. एक प्रश्न का उत्तर देने के लिए, उम्मीदवार को प्रत्येक प्रश्न के लिए सही उत्तर/सर्वोत्तम विकल्प खोजना होगा।
चतुर्थ। हालाँकि, key की चुनौती की प्रक्रिया के बाद, यदि एक से अधिक विकल्प सही पाए जाते हैं तो सभी/कोई
चिह्नित किए गए एकाधिक सही/सर्वोत्तम विकल्पों में से एक को चार अंक (+4) दिए जाएंगे।
किसी भी गलत विकल्प को चिह्नित करने पर माइनस एक अंक (-1) दिया जाएगा।
अनुत्तरित / अनुत्तरित प्रश्नों को कोई अंक नहीं दिया जाएगा।
यदि कोई प्रश्न छोड़ दिया जाता है / अनदेखा किया जाता है, तो सभी उम्मीदवारों को चार अंक (+4) दिए जाएंगे, इस तथ्य के बावजूद कि उम्मीदवार द्वारा प्रश्न को प्रत्याशी द्वारा किया गया है या नहीं I
Mode of Examination
NEET (UG) – 2021 is a Pen & Paper-based Test, to be answered on the specially designed
machine gradable OMR sheet using Ball Point Pen.
परीक्षा का तरीका
NEET (UG) – 2021 एक पेन और पेपर-आधारित टेस्ट है, जिसका उत्तर विशेष रूप से डिज़ाइन किए गए पर दिया जाना हैI बॉल प्वाइंट पेन का उपयोग कर मशीन ग्रेडेबल ओएमआर शीट।
Duration of Test
The duration of the test would be three (03) hours.
परीक्षण की अवधि
परीक्षण की अवधि तीन (03) घंटे होगी।
Medium of the Question Papers: -English Hindi Assamese Bengali Gujarati Malayalam Kannada
Marathi Odia Tamil Telugu Urdu Punjabi
प्रश्न पत्रों का माध्यम:-अंग्रेजी हिंदी असमिया बंगाली गुजराती मलयालम कन्नड़
मराठी ओडिया तमिल तेलुगु उर्दू पंजाबी
1 Candidates can opt for a Question Paper in any one of the following 13 languages:
2. Option of medium of Question Paper should be carefully chosen while filling in the
Application Form. The option once chosen cannot be changed.
3. Candidates opting for English would be provided Test Booklet in English only.
4. Candidates opting for Hindi would be provided with a Bilingual Test Booklet in
English and Hindi.
5. Candidates opting for Regional languages would also be provided with a Bilingual
Test Booklet in selected Regional language and English.
6. In case of any ambiguity in translation of a question in the test, its English version
shall be treated as final and the decision of NTA shall be final in this regard.
7. Option of Regional languages will be available as per the following table only: –
8. Candidates qualifying NEET (UG) – 2021 would be eligible for All India Quota and other
quotas under the State Governments/Institutes, irrespective of the medium of the
examination, subject to other eligibility criteria.
1. उम्मीदवार निम्नलिखित 13 भाषाओं में से किसी एक में प्रश्न पत्र का विकल्प चुन सकते हैं:
2. प्रश्न पत्र के माध्यम के विकल्प को भरते समय सावधानी से चुना जाना चाहिए
आवेदन फार्म। एक बार चुने गए विकल्प को बदला नहीं जा सकता।
3. अंग्रेजी का विकल्प चुनने वाले उम्मीदवारों को केवल अंग्रेजी में टेस्ट बुकलेट प्रदान की जाएगी।
4. हिंदी का विकल्प चुनने वाले उम्मीदवारों को एक द्विभाषी परीक्षण पुस्तिका प्रदान की जाएगी
अंग्रेजी और हिंदी।
5. क्षेत्रीय भाषाओं का चयन करने वाले उम्मीदवारों को द्विभाषी भी प्रदान किया जाएगा
चयनित क्षेत्रीय भाषा और अंग्रेजी में टेस्ट बुकलेट।
6. परीक्षण में किसी प्रश्न के अनुवाद में किसी भी अस्पष्टता के मामले में, इसका अंग्रेजी संस्करण
अंतिम माना जाएगा और इस संबंध में एनटीए का निर्णय अंतिम होगा।
7. क्षेत्रीय भाषाओं का विकल्प निम्न तालिका के अनुसार ही उपलब्ध होगा:-
8 एनईईटी (यूजी) – 2021 क्वालीफाई करने वाले उम्मीदवार अखिल भारतीय कोटा और अन्य के लिए पात्र होंगे I राज्य सरकारों/संस्थानों के तहत कोटा, माध्यम के बावजूद परीक्षा, अन्य पात्रता मानदंडों के अधीन।
Medical Entrance Exam will be conducted on 12 September 2021 with following Cororna Covid 19 Protocol. Online applications process will begin from 5.00 pm tomorrow i.e.13.07. 2021, through NTA website. In order to ensure social distancing norms, number of cities where examination will be conducted has been increased from 155 to 198.The number of Examination Centre will also be increased from the 3862 center’s used in 2020.- Twitted by Mr. Dharmendra Pradhan, Indian central Government Education minister Minister on 6.13 pm today i.e. 12.07.2021
For detailed information about visit NEET on following website address- https://ntaneet.nic.in
मेडिकल प्रवेश परीक्षा 12 सितंबर 2021 को कोरोना कोविड 19 प्रोटोकॉल का पालन करते हुए आयोजित की जाएगी। ऑनलाइन आवेदन प्रक्रिया एनटीए की वेबसाइट के माध्यम से कल, 13.07.2021 को शाम 5.00 बजे से शुरू होगी। सामाजिक दूरी के मानदंडों को सुनिश्चित करने के लिए, जिन शहरों में परीक्षा आयोजित की जाएगी, उनकी संख्या 155 से बढ़ाकर 198 कर दी गई है। परीक्षा केंद्रों की संख्या भी 2020 में उपयोग किए गए 3862 केंद्रों से बढ़ाई जाएगीI – आज शाम यानि 12.07.2021को 6.13 बजे श्री धर्मेंद्र प्रधान,शिक्षा, कौशल विकास और उद्यमिता मंत्री (भारतीय केंद्र सरकार) द्वारा ट्वीट किया गया I
एनईईटी के बारे में विस्तृत जानकारी के लिए निम्नलिखित वेबसाइट पते पर जाएं- https://ntaneet.nic.in
First 100 participants of quiz will get certificate if they score is 60% or more. CLICK HERE TO GIVE QUIZ
प्रश्नोत्तरी के पहले 100 प्रतिभागियों को प्रमाण पत्र मिलेगा यदि उनका स्कोर 60% या उससे अधिक है। CLICK HERE FOR QUIZ
Approximate population of world on 10 July 2021- 7,908,880,525 (7.90Billion)
10 जुलाई 2021 को विश्व की अनुमानित जनसंख्या :- 7,908,880,525 ( 7 अरब 90 करोड)
| The expected world population in 2030 is, 2030 में विश्व की अपेक्षित जनसंख्या होगी | 8 Billion |
| The expected world population in 2040 is, 2040 में विश्व की अपेक्षित जनसंख्या होगी | 9 billion |
| The expected world population in 2030 is, 2050 में विश्व की अपेक्षित जनसंख्या होगी | 10 billion |
One person added to world — — in every 0.39 Second संसार में एक व्यक्ति जोड़ा जाता है। – — प्रत्येक 0.39 सेकंड में
World population day is celebrated to create awareness to control population, family planning, gender equality, poverty, mental health and human right. विश्व जनसंख्या दिवस जनसंख्या नियंत्रण, परिवार नियोजन, लैंगिक समानता, गरीबी, मानसिक स्वास्थ्य और मानव अधिकार के प्रति जागरूकता पैदा करने के लिए मनाया जाता है।
| World Population Analysis विश्व जनसंख्या विश्लेषण | |
|---|---|
| Births per Day in the world विश्व में प्रति दिन जन्म | 382,865 |
| Deaths per Day in the world विश्व में प्रतिदिन होने वाली मृत्यु | 163,925 |
| Net increase in world population per Day प्रति दिन विश्व जनसंख्या में शुद्ध वृद्धि | 218,940 |

424 people in 1 square kilometer in India

1127 people in 1 square kilometer in Baangladesh
| Compare the parameters मापदंडों की तुलना | China चीन | India भारत | Pakisan पाकिस्तान | USA अमेरिका |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population जनसंख्या | 1.444 Billion 144 Crores | 1.393 Billion 139 crores | 0.225 Billion ( 22 crores) | 0.332 Billion ( 33 Crores) |
| Population density- Persons per square Kilometre आबादी घनत्व- व्यक्ति प्रति वर्ग किलोमीटर | 149 | 424 | 255 | 36 |
| Population Growth rate जनसंख्या विकास दर | 0.34% | 0.97% | 1.95% | 0.58 |
| % of World Population विश्व की % आबादी जनसंख्या | 18.34% | 17.69% | 2.86% | 4.23% |
| World Level Rank in Population विश्व स्तरीय जनसंख्या स्थिति | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
| Compare the parameters मापदंडों की तुलना | Indonesia इंडोनेशिया | brazil ब्राजील | Bangladesh बांग्लादेश | Russia रूस |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population जनसंख्या | 0.276Billion 27 Crores | 0.214 Billion 139 crores | 0.166 Billion ( 16 crores) | 0.145 Billion ( 14 Crores) |
| Population density- Persons per square Kilometre आबादी घनत्व- व्यक्ति प्रति वर्ग किलोमीटर | 145 | 25 | 1127 | 9 |
| Population Growth rate जनसंख्या विकास दर | 1.04 % | 0.67 % | 0.98 % | -0.02 |
| % of World Population विश्व की % आबादी जनसंख्या | 3.51 % | 2.27 % | 2.11 % | 1.85 % |
| World Level Rank in Population विश्व स्तरीय जनसंख्या स्थिति | 4 | 6 | 8 | 9 |
INDIA


In 2030, India is expected to be most populous country of the world and in 2060 the population of India will reach its peak of 1.65 billion people. 2030 में सात अरब भारत दुनिया का सबसे अधिक आबादी वाला देश होने की उम्मीद है और 2060 में भारत की जनसंख्या 1.65 अरब लोगों के अपने चरम पर पहुंच जाएगी I
After China and India which have the population more than 1 billion and hold position 1st and 2nd in the world, the next 11 countries are the most populous in the world and each have populations exceeding 100 million. Which are the United States, Indonesia, Brazil, Pakistan, Nigeria, Bangladesh, Russia, Mexico, Japan, Ethiopia, and the Philippines. Of these nations, all are expected to continue to grow except Russia and Japan, which will see their populations drop by 2030 before falling again significantly by 2050.
The smallest population in the world can be found in Vatican City, where only 801 people reside.
चीन और भारत के बाद जिनकी आबादी 1 अरब से अधिक है और दुनिया में पहले और दूसरे स्थान पर हैं, अगले 11 देश दुनिया में सबसे अधिक आबादी वाले हैं और प्रत्येक की आबादी 100 मिलियन से अधिक है, जो संयुक्त राज्य अमेरिका, इंडोनेशिया, ब्राजील, पाकिस्तान, नाइजीरिया, बांग्लादेश, रूस, मैक्सिको, जापान, इथियोपिया और फिलीपींस हैं। इन देशों में से, रूस और जापान को छोड़कर सभी के बढ़ने की उम्मीद है, जिन की जनसख्या 2030 तक लगार कम होगी और उसके बाद 2050 तक बहुत अधिक काम होगी।
दुनिया में सबसे छोटी आबादी वेटिकन सिटी में पाई जा सकती है, जहां केवल 801 लोग रहते हैं।
Drawbacks of population growth जनसंख्या वृद्धि से होने वाले नुकसान
जनसंख्या वृद्धि से होने वाले नुकसान 1.प्रति व्यक्ति आय में कमी
2.जनसंख्या पूंजी निर्माण की दर को कम करती है: – लगभग 40 से 50 प्रतिशत आबादी अनुत्पादक आयु वर्ग में है जो केवल उपभोग करती है और कुछ भी उत्पादन नहीं करती है।
3.आवश्यक वस्तुओं की प्रति व्यक्ति कम उपलब्धता:- दालें, खाद्यान्न, सब्जियां, चीनी और कपड़ा–
4.बेरोजगारी की बड़ी समस्या -एक बड़ी आबादी पैदा करती है:- जनसंख्या में तेज वृद्धि का मतलब है कि बड़ी संख्या में लोग श्रम बाजार में आते हैं और जिनके लिए रोजगार उपलब्ध कराना संभव नहीं है।
5.जीवन की निम्न गुणवत्ता जो निरक्षरता, स्वास्थ्य सेवाओं और पीने योग्य पानी की कमी, मध्यम या गंभीर रूप से कम वजन वाले बच्चों द्वारा ज्ञान के अभाव में परिलक्षित होती है।
6. गरीब का अंतहीन चक्र
7.सार्वजनिक उपयोगिता सेवाओं पर बोझ:- जनसंख्या में तेजी से वृद्धि स्वास्थ्य देखभाल, शिक्षा, आवास (ग्रामीण और शहरी दोनों), जल आपूर्ति, स्वच्छता, बिजली, सड़क, रेलवे आदि जैसे सामाजिक बुनियादी ढांचे पर भारी बोझ डालती है।
8.बचत, निवेश और पूंजी निर्माण पर प्रतिकूल प्रभाव I मिलियन-अरबों को खिलाने के लिए एक विशाल राजस्व सृजन की आवश्यकता है।
9.अनुत्पादक उपभोक्ताओं का भार:- अधिकतर वे 15 वर्ष से कम आयु के बच्चे और 60 वर्ष से अधिक आयु के वृद्ध व्यक्ति होते हैं।
10.पर्यावरण का ह्रास: प्राकृतिक संसाधनों के अत्यधिक उपयोग और कचरे के उत्पादन से जैव विविधता का नुकसान होता है, वायु और जल प्रदूषण होता है और भूमि पर दबाव बढ़ जाता है, अत्यधिक वनों की कटाई से जल जनित रोग जैसे दस्त, आंतों के कीड़े, हेपेटाइटिस आदि होते हैं। 11.आत्मनिर्भरता में बाधा:- लाखों की बढ़ती हुई जरूरतों को पूरा करने के लिए अधिक खाद्य पदार्थों की आवश्यकता जो निर्यात में कटौती करती है और विदेशी मुद्रा भंडार में कमी की ओर ले जाती है।
12.कृषि विकास की घटती प्रवृत्ति:-बड़ी जनसंख्या भूमि-पुरुष अनुपात को बिगाड़ती है अर्थात प्रति व्यक्ति खेती के लिए भूमि की उपलब्धता कम हो जाती है।
This question bank is available on http://www.chemigod.com
Answers are given in the end of questions.
(a) Negative deviation from Raoult’s law
(b) No deviation from Raoult’s law
(c) Positive deviation from Raoult’s law
(d) Positive or negative deviation from Raoult’s law depending upon the composition
3 . Out of molality (m), molarity (M), formality (F) and mole fraction (x), those which terms are independent of temperature are
(a) Molarity and molality
(b) Formality and and mole fraction
(c) molality and mole fraction
(d) Molarity and mole fraction
5.Dissolving 120 g of urea (mol. wt. 60) in 1000 g of water gave a solution of density 1.15 g/mL. The molarity of the solution is [IIT JEE 2011]
(a) 1.78 M
(b) 2.00 M
(b) 2.05 M
(d) 2.22 M
8.Equimolar solution in the same solvent have [AIEEE 2005]
(a) Same boiling point but different freezing point
(b) Same freezing point but different boiling point
(c) Same boiling point and same freezing point
(d) Different boiling point and different freezing point
Answers–
1.(c) 0.20
2.(a) Negative deviation from Raoult’s law
3.(c) molality and mole fraction
4.(d) Formation of an azeotropic mixture
5.(b) 2.05 M
6.(b) Positive deviation from Raoult’s Law.
7.(b) 0.1 M Urea
8.(c) Same boiling point and same freezing point
9.b) 0.1 M Urea
10.(c) 0.3 × 10-2
Answers are given in the end of questions.
This question bank is available on http://www.chemigod.com
Which one of the following is non-crystalline or amorphous?
(a) Diamond
(b) Graphite
(c) Glass
(d) Common Salt
The crystal with metal deficiency defect is
(a) NaCl
(b) FeO
(c) KCl
(d) ZnO
Which type of defect has the presence of cations in the interstitials sites?
(a) Schottky defect
(b) Vacancy defect
(c) Frenkel defect
(d) Metal deficiency defect
NaCl type crystal (with coordination no. 6 : 6) can be converted into CsCl type crystal (with coordination no. 8 : 8) by applying
(a) high temperature
(b) high pressure
(c) high temperature and high pressure
(d) low temperature and low pressure
Which of the following metal oxides is antiferromagnetic in nature?
(a) MnO2
(b) TiO2
(c) VO2
(d) CrO2
An element with atomic mass 100 has a bcc structure and edge length 400 pm. The density of element is
(a) 10.37 g cm-3
(b)2.14 g cm-3 (c) 7.29 g cm-3
(d) 5.19 g cm-3
Alkali halids do not show Frenkel defect because
(a) cations and anions have almost equal size
(b) there is a large difference in size of cations and anions
(c) cations and anions have low coordination number
(d) anions cannot be accommodated in voids
Which of the following compound is metallic and ferromagnetic?
(a) CrO2
(b) VO2
(c) MnO2
(d) TiO2
Which one of the following is a molecular crystal?
(a) Rock salt
(b) Quartz
(c) Dry ice
(d) Diamond
The density of a metal which crystallises in bcc lattice with unit cell edge length 300 pm and molar mass 50 g mol-1 will be
(a) 10 g cm-3
(b) 14.2 g cm-3
(c) 6.15 g cm-3
(d) 9.3 2 g cm-3
Answer:-
(c) Glass
(b) FeO
(c) Frenkel defect
(b) high pressure
(a) cations and anions have almost equal size
(a) CrO2
(a) MnO2
(d) 5.19 g cm-3
(c) Dry ice
(c) 6.15 g cm-3
Click on Quiz to participate
भाग लेने के लिए प्रश्नोत्तरी शब्द पर क्लिक करें


| PAGE | Link button |
|---|---|
| A list of pages with links लिंक वाले पृष्ठों की सूची | CLICK HERE |
| SIddharth Siyag,Engineer from JNV, Bikaner सिद्धार्थ सियाग, इंजीनियर जेएनवी, बीकानेर से | CLICK HERE |
| Azruddin Laad, Asistant Professor (Guest Faculty) from JNV, Bikaner अजरुद्दीन लाड, असिस्टेंट प्रोफेसर (अतिथि संकाय ) जेएनवी, बीकानेर से | CLICK HERE |
| ???………………………………………………….. THIS IS FOR YOU यह आपके लिए है | See below for kind invitation विनम्र आमंत्रण के लिए नीचे देखें |
Download from here–>
JAWAHAR NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA ………………, Distt. ………….., (……)
AISSCE-2023
CHEMISTRY PRACTICAL PAPER
Time : 3 hours Date:- M.M. : 30
Instructions :
Q1. Find out the molarity and strength in g/L of given KMnO4 solution by using M/20 Mohr salt solution.
Or Find out the molarity and strength in g/L of given KMnO4 solution by using M/20 oxalic acid solution. (8)
Q2. To detect the presence of one cation and one anion in given salt. (8)
Q3. Identify the functional group present in the given organic compound. (6)
Q4. Investigatory Project and viva voice (4)
Q5. Class record and viva-voice (4)
Marking Scheme:
Total 30
Sign of Internal Examiner Sign of External Examiner
Name: Name:-
PGT Chemistry PGT Chemistry
An azeotrope, also known as a constant boiling point mixture, comprises two or more components in fluidic states, wherein their proportions cannot be modified through simple distillation. This occurs because during boiling, the vapor maintains the same composition as the original mixture. Understanding azeotropic behavior is crucial in fluid separation techniques.it is not possible to separate the components by fractional distillation and therefore, azeotropic distillation is usually used instead. (एज़ोट्रोप, जिसे निरंतर क्वथनांक मिश्रण के रूप में भी जाना जाता है, में तरल अवस्था में दो या दो से अधिक घटक शामिल होते हैं, जिसमें उनके अनुपात को सरल आसवन के माध्यम से संशोधित नहीं किया जा सकता है। ऐसा इसलिए होता है क्योंकि उबलने के दौरान वाष्प मूल मिश्रण के समान ही संरचना बनाए रखता है। द्रव पृथक्करण तकनीकों में एज़ोट्रोपिक व्यवहार को समझना महत्वपूर्ण है। आंशिक आसवन द्वारा घटकों को अलग करना संभव नहीं है और इसलिए, इसके बजाय आमतौर पर एज़ोट्रोपिक आसवन का उपयोग किया जाता हैI)
Each azeotrope has a characteristic boiling point. The boiling point of an azeotrope is either less than the boiling point temperatures of any of its constituents (a positive azeotrope), or greater than the boiling point of any of its constituents (a negative azeotrope). For both positive and negative azeotropes, (प्रत्येक एज़ोट्रोप का एक विशिष्ट क्वथनांक होता है। किसी एज़ोट्रोप का क्वथनांक या तो उसके किसी भी घटक (एक सकारात्मक एज़ोट्रोप) के क्वथनांक तापमान से कम होता है, या उसके किसी भी घटक (एक नकारात्मक एज़ोट्रोप) के क्वथनांक से अधिक होता है। सकारात्मक और नकारात्मक दोनों एज़ोट्रोप के लिए, आंशिक आसवन द्वारा घटकों को अलग करना संभव नहीं है और इसके बजाय आमतौर पर एज़ोट्रोपिक आसवन का उपयोग किया जाता है।)
| Type of Azeotropic Mixture | Example | Boiling Point of Ethanol | Boiling Point of Water | Composition of Azeotropic Mixture | Boiling Point of Azeotropic Mixture |
| Minimum Boiling Azeotropes | Ethanol & water | 78.4 0C | 100 0C | 95.63& Ethanol & 4.37 Water by mass | 78.2 0C |
| Type of Azeotropic Mixture | Example | Boiling Point Nitric acid | Boiling Point of Water | Composition of Azeotropic Mixture | Boiling Point of Azeotropic Mixture |
| Maximum Boiling Azeotropes | Nitric and water | 83 0C | 100 0C | 68% nitric acid and 32% water by mass | 120.5°C |
| Type of Azeotropic Mixture | Example | Boiling Point Hydrochloric acid | Boiling Point of Water | Composition of Azeotropic Mixture | Boiling Point of Azeotropic Mixture |
| Maximum Boiling Azeotropes | Hydrochloric acid and Water | -85 0C | 100 0C | hydrochloric acid 20.2% and 79.8% water by mass | 120.4 °C (393.5 K) |
A solution of two liquids that shows greater positive deviation from Raoult’s law forms a minimum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition. In general, a positive azeotrope boils at a lower temperature than boiling temperature of any other ratio of its constituents. Positive azeotropes are also called minimum boiling mixtures. A well-known example of a positive azeotrope is an ethanol–water mixture (obtained by fermentation of sugars) consisting of 95.63% ethanol and 4.37% water (by mass), which boils at 78.2 °C. Ethanol boils at 78.4 °C, water boils at 100 °C, but the azeotrope boils at 78.2 °C, which is lower than either of its constituents. Once this composition has been achieved, the liquid and vapour have the same composition, and no further separation occurs.(दो तरल पदार्थों का एक समाधान जो राउल्ट के नियम से अधिक सकारात्मक विचलन दिखाता है, एक विशिष्ट संरचना पर न्यूनतम उबलते एज़ियोट्रोप बनाता है। सामान्य तौर पर, एक सकारात्मक एज़ोट्रोप अपने घटकों के किसी भी अन्य अनुपात के उबलते तापमान की तुलना में कम तापमान पर उबलता है। धनात्मक एज़ोट्रोप्स को न्यूनतम उबलने वाला मिश्रण भी कहा जाता है। सकारात्मक एज़ोट्रोप का एक प्रसिद्ध उदाहरण इथेनॉल-पानी का मिश्रण (शर्करा के किण्वन द्वारा प्राप्त) है जिसमें 95.63% इथेनॉल और 4.37% पानी (द्रव्यमान द्वारा) होता है, जो 78.2 डिग्री सेल्सियस पर उबलता है। इथेनॉल 78.4 डिग्री सेल्सियस पर उबलता है, पानी 100 डिग्री सेल्सियस पर उबलता है, लेकिन एज़ियोट्रोप 78.2 डिग्री सेल्सियस पर उबलता है, जो इसके किसी भी घटक से कम है। एक बार यह संरचना प्राप्त हो जाने के बाद, तरल और वाष्प की संरचना समान हो जाती है, और आगे कोई पृथक्करण नहीं होता है।)
A solution that shows large negative deviation from Raoult’s law forms a maximum boiling azeotrope at a specific composition. Nitric acid and water is an example of this class ( negative deviation ) of azeotrope. This azeotrope has an approximate composition of 68% nitric acid and 32% water by mass, with a boiling point of 393.5 K (120.4 °C). A negative azeotrope boils at a higher temperature than any other ratio of its constituents. Negative azeotropes are also called maximum boiling mixtures azeotropes. Another example of a negative azeotrope is hydrochloric acid at a concentration of 20.2% and 79.8% water (by mass). Hydrogen chloride boils at -85 °C and water at 100 °C, but the azeotrope boils at 110 °C, which is higher than either of its constituents. (एक समाधान जो राउल्ट के नियम से बड़ा नकारात्मक विचलन दिखाता है, एक विशिष्ट संरचना पर अधिकतम उबलता हुआ एज़ोट्रोप बनाता है। नाइट्रिक एसिड और पानी एज़ोट्रोप के इस वर्ग (नकारात्मक विचलन) का एक उदाहरण है। इस एज़ोट्रोप में द्रव्यमान के हिसाब से 68% नाइट्रिक एसिड और 32% पानी की अनुमानित संरचना होती है, जिसका क्वथनांक 393.5 K (120.4 डिग्री सेल्सियस) होता है। एक नकारात्मक एज़ोट्रोप अपने घटकों के किसी भी अन्य अनुपात की तुलना में उच्च तापमान पर उबलता है। नकारात्मक एज़ोट्रोप्स को अधिकतम क्वथनांक मिश्रण एज़ोट्रोप्स भी कहा जाता है। नकारात्मक एज़ोट्रोप का एक अन्य उदाहरण 20.2% और 79.8% पानी (द्रव्यमान द्वारा) की सांद्रता पर हाइड्रोक्लोरिक एसिड है। हाइड्रोजन क्लोराइड -85 डिग्री सेल्सियस पर और पानी 100 डिग्री सेल्सियस पर उबलता है, लेकिन एज़ोट्रोप 110 डिग्री सेल्सियस पर उबलता है, जो इसके किसी भी घटक से अधिक है।)
When phenol is treated with chloroform (CHCl3) in presence of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to produce salicylaldehyde ( ortho Hydroxybenzaldehyde) is known as Reimer Tiemann,s Reaction.
This reaction is actually formylation (Addition of -CHO group) of phenol at ortho position.
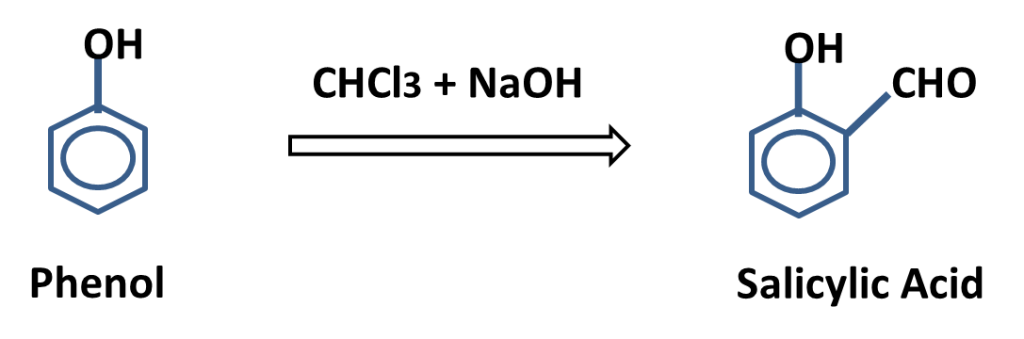
Short Mechanism:-
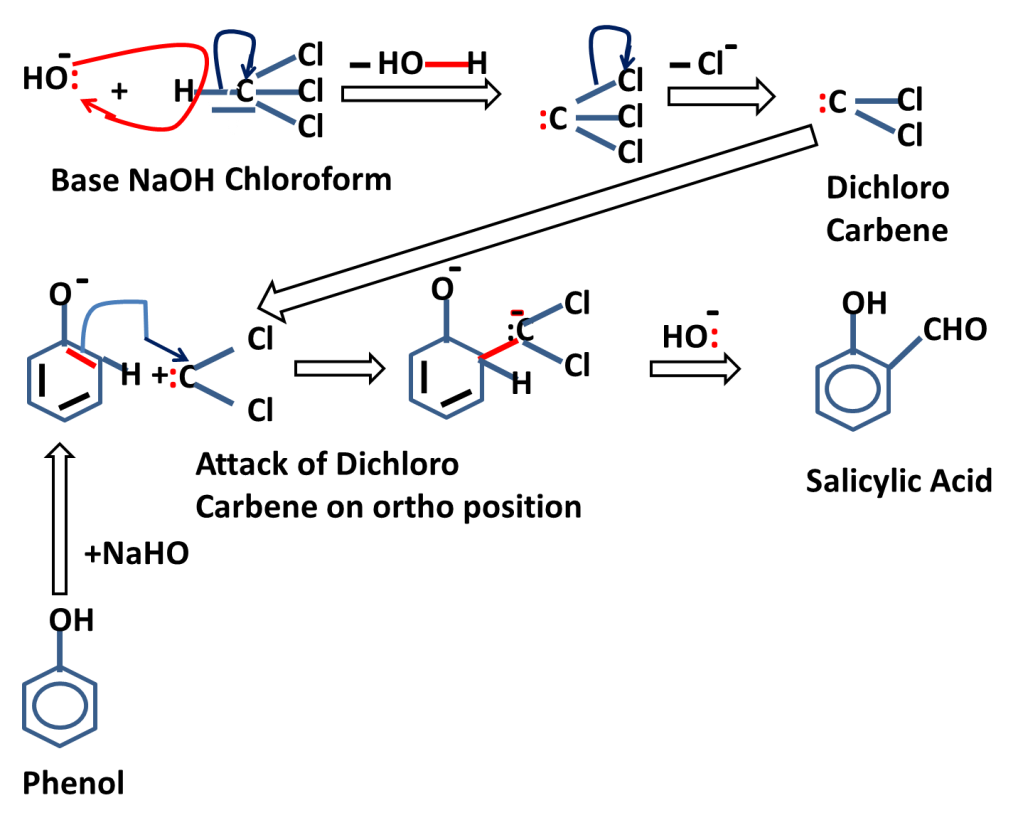
The reaction in which Phathalimide is treated with sodium hydroxide, haloalkane to produce primary aliphatic amine is known as Gabriel Phthalimide Reaction.
Pure primary amine is obtained in this reaction as its separation is easy.
NOTE-Aryl Amine can not prepared by this reaction as aryl halide does not undergo nucleophylic substitution.