Question:-Explain the paramagnetic nature of oxygen and calculate bond order by drawing molecular orbital orbital diagram and molecular orbital electronic configuration.
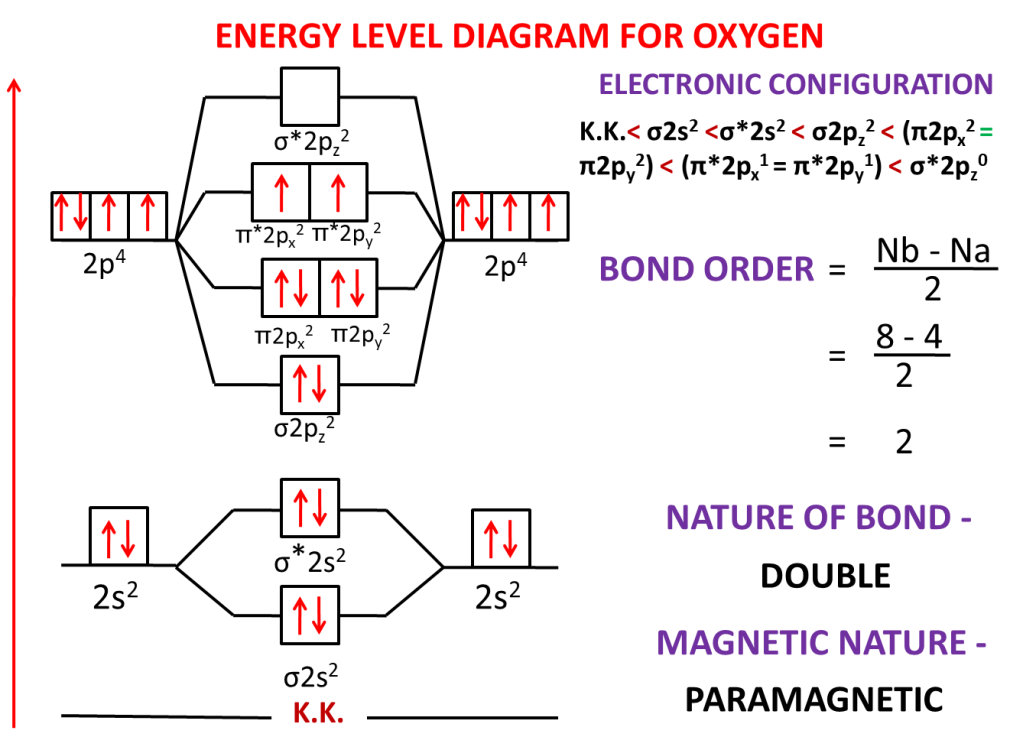
Question:-Explain the paramagnetic nature of oxygen and calculate bond order by drawing molecular orbital orbital diagram and molecular orbital electronic configuration.

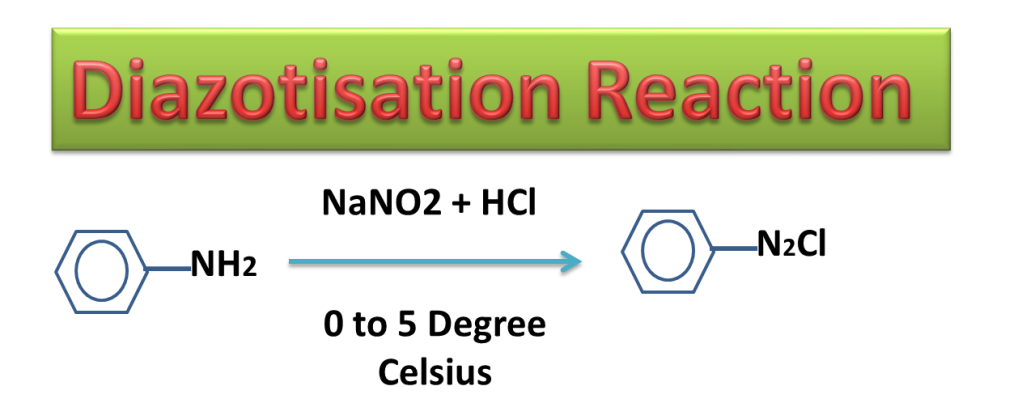
In diazotization Reaction, The aniline is treated with nitrous acid ( a mixture of sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid) at temperature 00 to 50 Celsius ( 273 K to 278 K ) to produce diazonium chloride.
Nitrous acid is produce in the reaction mixture by treating NaNO2 with HCl
NaNO2 + HCl —> HNO2 + NaCl
Diazonium salt is highly unstable and can explode at little higher temperature therefore it is prepared at lower temperature (00 to 50 Celsius).
Diazonium salt can not be separated and product mixture is used for further reaction because diazonium salt is highly unstable and explode on distillation (on heating).
Diazonium salt is very much important in organic synthesis as for preparation of large number of organic compounds, it is precursor (Reactant).
Aldehydes Ketones and Ethers:- Important and conceptual questions
Answers are given in the end-
1. Why does carbonyl compounds give Nucleophylic reaction?
2. Arrange the following carbonyl compounds in increasing order of their reactivities towards nucleophylic addition reaction.
CH3CHO, HCHO, CH3COCH3
3.Which of the following compounds give iodoform reaction and why?
CH3CHO, HCHO, CH3CH2COCH2CH3
4 Which of the following compounds give cannizaro,s reaction and why?
CH3CHO, HCHO, CH3CH2COCH2CH3
5. Which of the following compounds give aldol condensation reaction and why?
CH3CHO, HCHO, CH3CH2COCH2CH3
6. How many compounds are formed in the cross aldol condensation of
A) CH3CHO, CH3COCH3
B) Ph-CHO and CH3CHO
C) Ph-CO-Ph and CH3CHO
D) CH3COCH3 and CH3CH2COCH2CH3
E) Ph-CHO and Ph-CO-Ph
7.What are the disproportion reaction. Give example.
Answer-
1. Nucleophylic reaction reaction occure due to presence of partial positive charge on carbonyl carbon and addition reaction occure due to presence of double bond.
2. CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO < HCHO
3. CH3CHO, The compounds have three alpha hydrogen atoms to carbonyl groups gives iodoform reaction.
4. HCHO, The compounds have no any alpha hydrogen atoms to carbonyl groups gives cannizaro,s reaction.
5. CH3CHO and CH3CH2COCH2CH3 The compounds have atleast one alpha hydrogen atoms to carbonyl groups gives aldol condensation reaction.
6. A) Four aldol products
B) Two aldol products
C)Two aldol products
D) Four aldol products
E) No aldol products
7. The reaction in which same species is oxidized and reduced simultaneously.
Example is cannizaro,s reaction in which carbonyl compounds having no alpha hydrogen is oxidized in carboxylate ion and reduced to alcohol.
Ph-CHO + KOH à Ph-COO– + Ph-CH2-OH
Answers are given in the end-
1. How will you distinguish butanol, butan-2-ol and 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
2. How will you distinguish aniline and phenol?
3.How will you distinguish phenol and ethanol?
4.How will you distinguish ethanamine and N-Methyl methanine.
5.How will you distinguish Propanamine and N,N-Dimethylethanamine.
6.How will you distinguish Propanamine, N-Methyethanamine and N,N-Dimethylmethanamine.
7. How will you distinguish Ethanol and Ethanoic acid.
8.How will you distinguish Methanal and Ethanal?
9.How will you distinguish Propanal and Propanol.
10.How will you distinguish Propanol and Ethanol?
11.How will you distinguish Choloromethane and Chlorobenzene.
Answer-
1.When Licas reagent (ZnCl2 + HCl ) is added than turbidity appears immediately in Methylbutan-2-ol ( tertiary alcohol), turbidity appears after 5 minutes in butan-2-ol ( Secondary alcohol) and no turbidity appears in butanol ( Primary alcohol).
2.Phenol gives violet colour with neutral FeCl3 while aniline does not.
3.Ethanol gives red colour with ceric ammonium nitrate while phenol does not.
4.Ethanamine reacts with benzenesulphonyl chloride( Hinesburg’s Reagent) which is soluble in dilute solution of NaOH, whereas N-Methyl methanine reacts but insoluble in dilute solution of NaOH.
5.Propanamine reacts with benzenesulphonyl chloride ( Hinesburg’s Reagent) which is soluble in dilute solution of NaOH, whereas N,N-Dimethylethanamine does not react.
6.Propanamine reacts with benzenesulphonyl chloride ( Hinesburg’s Reagent) which is soluble in dilute solution of NaOH whereas N-Methyl ethanine reacts but insoluble in dilute solution of NaOH whereas N,N-Dimethylethanamine does not react.
7.Ethanol gives red colour with ceric ammonium nitrate while Ethanoic acid does not.
Or Ethanol gives frutty smell of esters with ethanoic acid and few drops of conc. H2SO4 whereas ethanoic acid does not. (Note- This is ester test)
8.Ethanal gives yellow ppt with a mixture of NaOH and I2 while methanol does not ( Iodoform,s Test)
9.Propanal gives silver mirror or black ppt with Tollen,s reagent( AgNO3 + NH4OH) while Propanol does not.
Or Propanal gives red ppt with mixture of Fehling,s solution A ( solution of CuSO4) and B ( solution of sodium potassium tartarate and NaOH) while Propanol does not.
( Note- Aldehydes gives Tollens test and Fehling,s solution test while ketones does not.)
10.Ethanol gives yellow ppt with a mixture of NaOH and I2 while propanol does not (Note-This is Iodoform,s Test given by compounds having three alpha hydrogen to carbonyl group or three beta hydrogen to alcoholic group)
11.Choloromethane gives white precipitate with AgNO3 but Chlorobenzene does not.