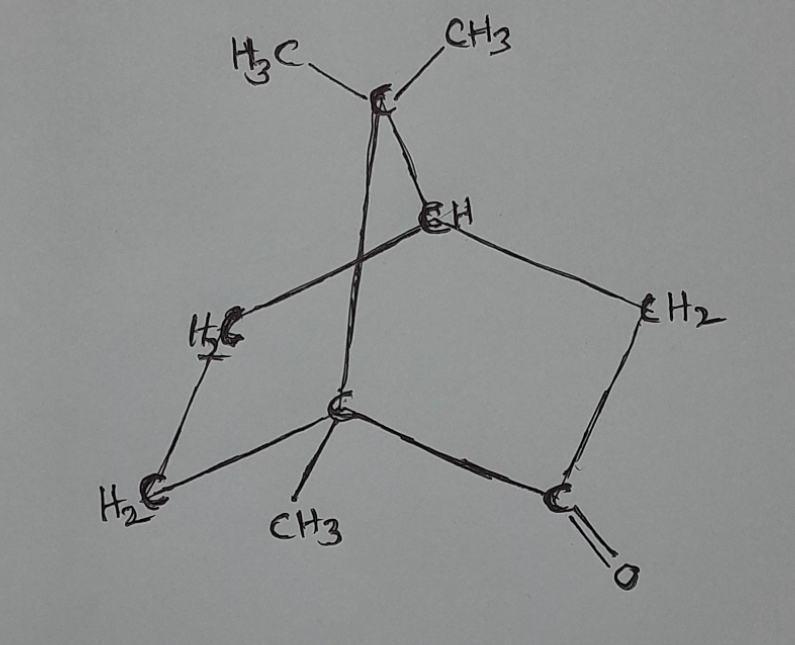
Camphor:-
Formula:-( C10H16O )
Structure:- bicyclic ketone ( Bicyclic means compounds containing two rings.)
Ketones is a functional group, in which one carbon has double bond with one oxygen and one-one single bond with other carbon atom.
Uses:-
1. It is burnt in worship.
2.As disinfectant, It produce lumps of carbon atoms which adsorb micro organism, particles of good or bad smell.
3.used on the skin as a painkiller in concentrations of 3% to 11%.
4.Camphor is used in many rub-on products to reduce pain related to cold sores, insect stings and bites, minor burns, and hemorrhoids.
5.It is used as one component of “amritdhara”
which is used to apply on forehead to relieve from headache.
6. It is used in products such as Vicks Vapo Rub.
7.Warning:-Oral camphor is unsafe. It is also important not to apply camphor to broken skin, because it can enter the body quickly and reach concentrations that are high enough to cause poisoning.
Source:-
1. Camphor is present in the volatile oils of camphor obtained from tree- Cinnamomum camphora ( Botanical Name ), or Camphor laurel
2.These days, camphor is usually manufactured from turpentine oil.
Process of making:- Camphor is obtained by using steam distillation of wood, twigs and bark of the Camphor tree, followed by purification and sublimation.
Occurrence of Camphor Tree:- In India, South east China, Taiwan, Japan, Mangolia, Indonesia.
Height:- 50- 60 feet ( 15 -18 metre )
Age :- 150 Years
Shape:- Umbrella
Width:- Up to 15 m
कपूर / या कर्पूरम :-
फॉर्मूला:- (C10H16O)
संरचना:- द्विचक्रीय कीटोन
( द्विचक्रीय वलय का अर्थ है दो वलय वाले यौगिक)
कीटोन एक कार्यात्मक समूह है, जिसमें एक कार्बन का एक ऑक्सीजन के साथ दोहरा बंधन होता है और अन्य कार्बन परमाणुओं के साथ एक-एक एकल बंधन होता है।
उपयोग:-
1. इसे पूजा में जलाया जाता है।
2. निस्संक्रामक के रूप में, यह कार्बन परमाणुओं की गांठें उत्पन्न करता है जो सूक्ष्म जीवों, अच्छी या बुरी गंध के कणों को सोख लेती हैं।
3.त्वचा पर दर्द निवारक के रूप में 3% से 11% की सांद्रता में उपयोग किया जाता है।
4.इसका उपयोग कई रगड़-उत्पादों में ठंड घावों, कीड़े के डंक और काटने, मामूली जलन और बवासीर से संबंधित दर्द को कम करने के लिए किया जाता है।
5.यह “अमृतधारा” के एक घटक के रूप में प्रयोग किया जाता है, जिसे सिर दर्द से राहत पाने के लिए माथे पर लगाने के लिए प्रयोग किया जाता है।
6. इसका उपयोग विक्स वेपो रब जैसे उत्पादों में किया जाता है।
7. चेतावनी:- मुह के द्वारा इसे लेना असुरक्षित हैI यह भी महत्वपूर्ण है कि टूटी हुई त्वचा पर कपूर न लगाएं, क्योंकि यह शरीर में जल्दी से प्रवेश कर सकता है और इतनी अधिक मात्रा में सांद्रता तक पहुँच सकता है कि विषाक्तता पैदा कर सकता है।
स्रोत:-
1.कपूर पूर्व सिनामोमम कपूर (वानस्पतिक नाम) या कपूर लॉरेल के वाष्पशील तेलों में मौजूद होता है।
2.आजकल, कपूर आमतौर पर तारपीन के तेल से बनाया जाता है।
बनाने की प्रक्रिया:-
1.कपूर की लकड़ी, टहनियों और छाल के भाप आसवन का उपयोग करके कपूर प्राप्त किया जाता है, इसके बाद शुद्धिकरण और उर्ध्वपातन किया जाता है।
कपूर के पेड़ की उपस्थिति:- भारत, दक्षिण पूर्व चीन, ताइवान, जापान, मंगोलिया, इंडोनेशिया
ऊंचाई:- 50- 60 फीट (15-18 मीटर)
आयु :- 150 वर्ष
आकार:- छाता / छतरी का आकार
चौड़ाई:- 15 मी . तक

